FIGURE 1.
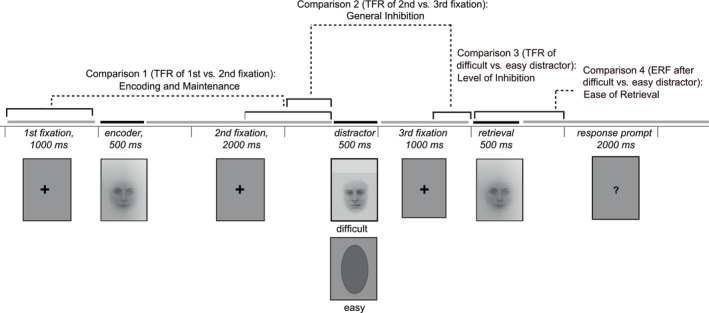
Experimental paradigm and examined contrasts. The encoder, distractor and target images were separated by visual presentation of fixation crosses lasting for 1000–2000 ms. After the target image, a question mark visually presented for 2000 ms prompted the participants to indicate with the button press whether the target image was identical or different than the encoder image. In the analyses of the oscillatory data, we examined neural processes related to encoding and maintenance by comparing the first to the second fixation window (1000 ms time windows), and related to inhibitory control by comparing the second to the third fixation window (500 ms time windows) and the third fixation window preceded by difficult distractor to the third fixation window preceded by easy distractor (500 ms time windows). In the analysis of the evoked data, we examined neural processes related to retrieval by comparing the matching target image preceded by difficult distractor to the matching target image preceded by easy distractor (time windows of 0–300, 300–500, and 500–700 ms after the presentation of the target image). TFR, time–frequency representation.
