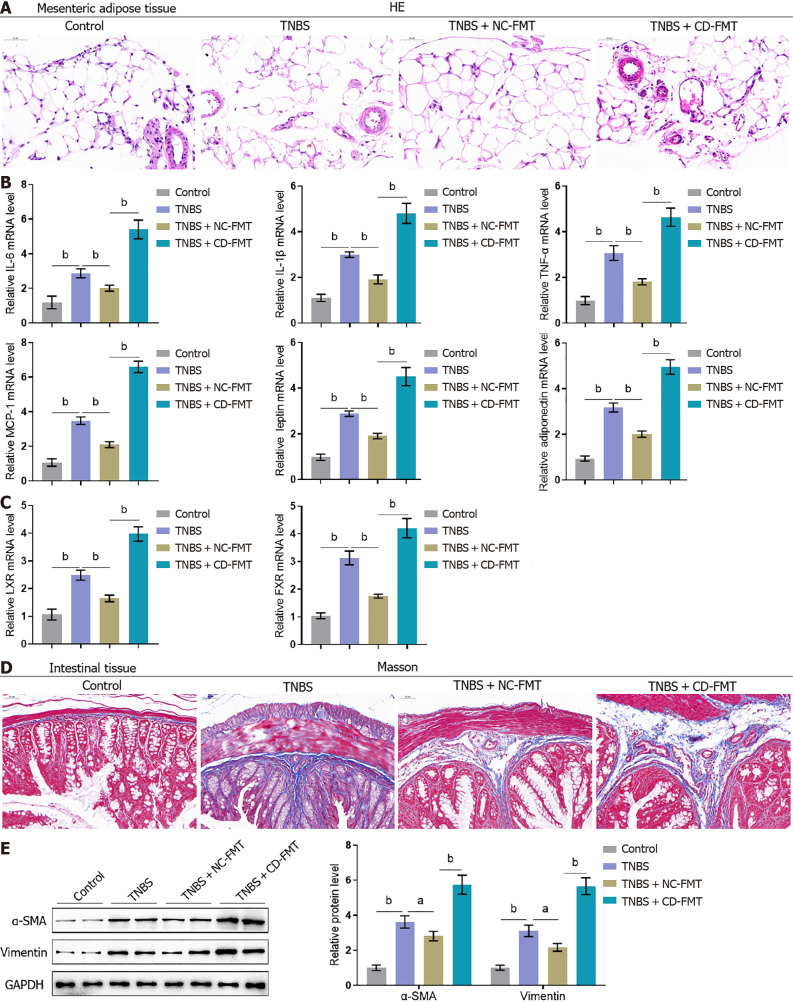
Figure 5.
Effects of gut microbiota from Crohn’s disease patients on the histopathological characteristics of mesenteric adipose and intestinal tissues from mice with 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced Crohn’s disease. A: Mesenteric adipose tissues collected from mice were stained with hematoxylin-eosin to assess histopathological alterations (× 150); B and C: Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assays of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1β, tumour necrosis factor alpha, MCP-1, leptin, adiponectin, LXR, and FXR mRNA levels in mouse tissues; D: Intestinal tissues from mice stained with Masson stain to evaluate fibrotic alterations (× 150); E: Immunoblotting assays of alpha-smooth muscle actin and vimentin protein levels in mouse intestinal tissues. n = 6 or 3, bP < 0.01 vs control; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) alone; bP < 0.01 vs TNBS + NC-fetal microbiota transplantation, by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD test. TNBS: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid; CD: Crohn’s disease; NC: Normal control; FMT: Fetal microbiota transplantation; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; α-SMA: Alpha-smooth muscle actin.