Figure 2.
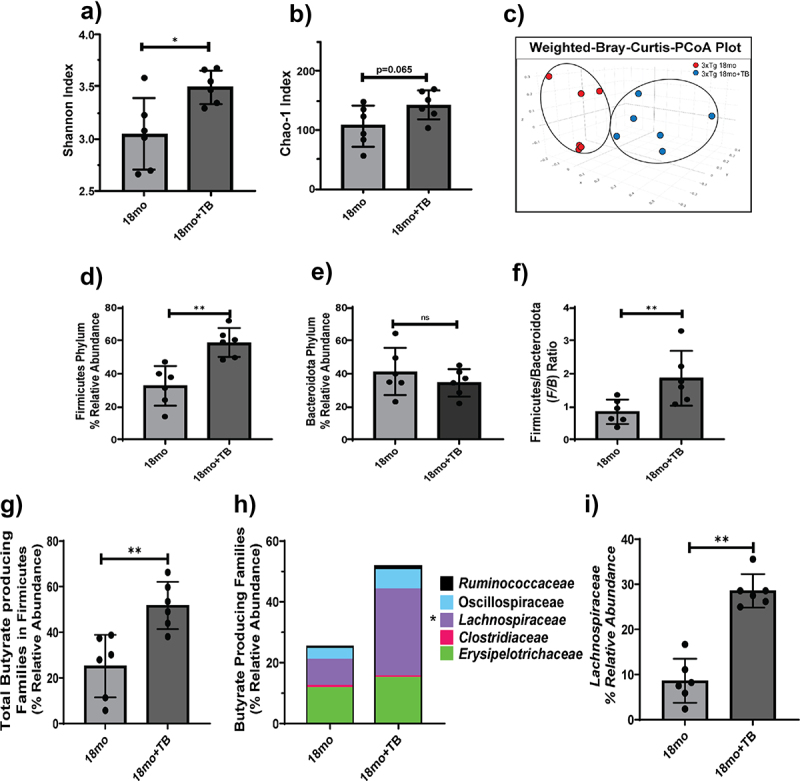
Oral administration of TB prevents the decrease in microbial diversity and composition in 18 month old 3×Tg mice.
Alpha diversity metrics Shannon Index a) and Chao-1 Index b) as well as Beta diversity PCoA plots c) are shown for 18 month old 3×Tg mice with and without TB treatment. The Beta diversity data are significant at p < 0.05, calculated using ADONIS (R vegan package). The relative abundance of communities from Firmicutes d), or Bacteroidota e) phyla, and the F/B ratio f) are shown. Butyrate-producing communities from the Firmicutes phylum are shown as total g) or indicated families in stacked bars h). The relative abundance of the Lachnospiraceae family, which harbors the most butyrate producers, is significantly increased in 18 month old 3×Tg given TB compared to no TB treatment i). Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 4–6). Student’s t-test statistical analysis was performed, and significance denoted as ns: not significant, *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01.
