Figure 4.
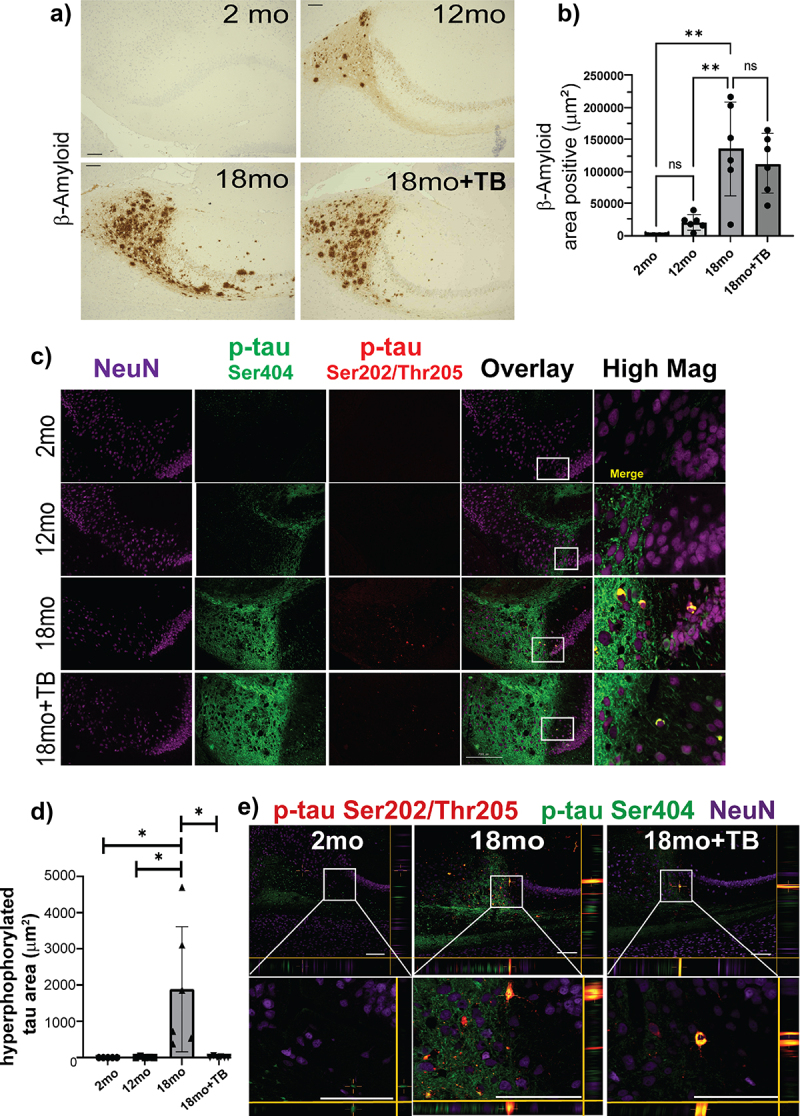
TB prevents hyper-phosphorylation of tau, a critical component of ad-like pathology in 3×Tg mice.
The presence of Aβ (Aβ40 or Aβ42) in the subiculum of sagittal brain sections was assessed by immunohistochemical staining by D12B2 mAb visualized using DAB. Representative images taken at 20× magnification (a) and area positive quantification using ImageJ (RRID:SCR_003070) are shown (b). To assess tau hyper-phosphorylation, sagittal brain sections were triple stained with two different p-tau mAb, D2Z4G-FITC (p-tauSer404, green), AT8-TRITC (p-tauSer202/Thr205, red) and anti-neuron mAb (NeuN-Cy5; purple). Representative images are shown (c). The images labeled as Overlay + NeuN and High Mag are merged fluorescent images with co-localization of the p-tau stains indicated in yellow. The area shown in the High Mag images is indicated in white boxes in the Overlay + NeuN images and is increased 4-fold. Area positive staining was determined for p-tau Ser404 and p-tau Ser202/Thr205 co-localization (d). The size bar = 200 µm. Bar graphs and error bars represent mean scores ± SD, and data from individual mice are shown as closed markers. Statistics were calculated using parametric ordinary one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons, and significance indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Representative confocal microscopy images of fluorescent staining demonstrating co-localization of p-tau stained, AT8 (red; Ser202/Thr205) and D2Z4G (green; Ser404), were significantly increased within subiculum NeuN-positive (purple) neurons of 3×Tg mice by 18 months e). XZ and YZ focal planes are shown to conclusively demonstrate co-localization of these two stains. Co-localized staining shown as yellow was reduced in 18mo+TB. White boxes in the top images are magnified in the lower boxes. Magnification bars = 100 μm.
