Figure 6.
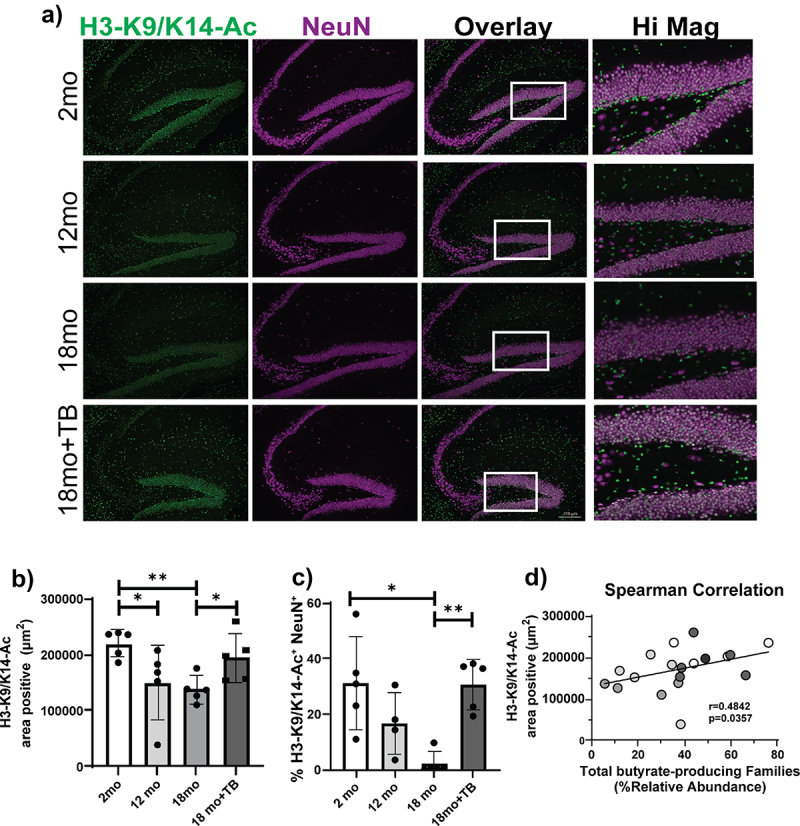
TB supplementation prevents the age-related decrease of H3K9/K14-ac in 3×Tg mice.
Representative images of K9/K14 acetylation of histone 3 in the hippocampus of indicated 3×Tg mice were assessed by immunofluorescent staining using anti-H3K9/K14Ac-FITC (green) and anti-NeuN-Cy5 (purple) antibodies. Double positive cells are shown (white) in the Overlay and Hi Mag panels a). Quantification of total H3K9/K14-Ac staining indicated as area positive staining b). The percent of neurons positive for H3K9/K14-Ac in the dentate gyrus was determined as area of H3K9/K14Ac-FITC and NeuN-Cy5 co-localization divided by the total area of NeuN-Cy5 staining c). Magnification bars = 200 μm (A, Overlay 18mo+TB, white bars on bottom right). Bar graphs and error bars represent mean scores ± SD, and data from individual mice are shown as closed circles. Statistics were calculated using non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test for multiple comparisons, and Mann-Whitney test for comparing 18 month with and without TB, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Non-parametric Spearman Correlation analysis plot demonstrates the linear association between % relative abundance of total butyrate-producing bacteria with H3K9/K14-Ac area positive staining d). Results from individual mice from all groups of 3×Tg are denoted by different colored circles (white: 2 months old; light gray: 12 months old; medium gray: 18 months old; and dark gray: TB-treated 18 months old). The Spearman correlation coefficient r = 0.4842 with P value significance p = 0.0357.
