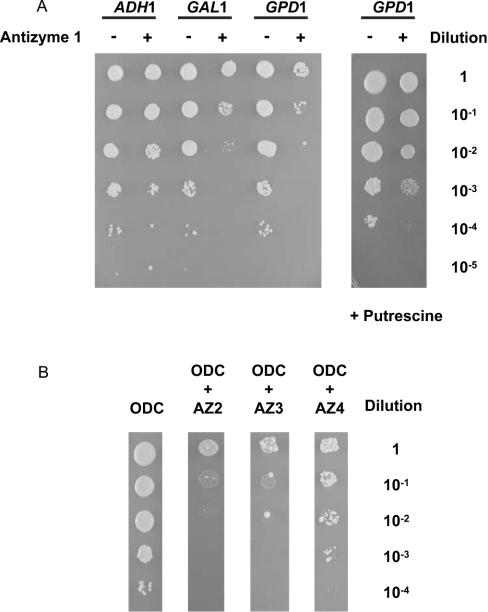
Figure 4. Functional expression of antizymes in yeast.
(A) Functional expression of antizyme 1 in yeast. Yeast cells deleted for spe1 (strain Y15034) were transformed with plasmid p413GALL-ODC (carrying human ODC behind the yeast GALL promoter) and either the control plasmids p426ADH (–), p426GAL1 (–) and p426GPD (–) or plasmids p426ADH-AZ1 (+), p426GAL1-AZ1 (+) or p426GPD-AZ1 (+) (carrying human antizyme 1 behind the yeast ADH1, GAL1 and GPD1 promoters respectively). Liquid cultures were grown overnight in selective polyamine-free glucose medium. The overnight cultures were adjusted to A600 3.0/ml and serial dilutions starting with 3.0/ml were spotted (2 μl aliquots) as indicated on polyamine-free selective galactose plates (left panel) or selective galactose plates containing 7.5 μM of putrescine (right panel). The plates were then incubated for 3 days at 30 °C. The colony assays shown are representative for multiple experiments. (B) Functional expression of antizymes 2–4 in yeast. Yeast cells deleted for spe1 (strain Y15034) were transformed with plasmid p413GALL-ODC alone (lane 1, carrying human ODC behind the yeast GALL promoter) or co-transformed with plasmid p426GAL1-AZ2 (lane 2, carrying antizyme 2 behind the yeast GAL1 promoter), p426GAL1-AZ3 (lane 3, carrying antizyme 3 behind the yeast GAL1 promoter) or p426GPD-AZ4 (lane 4, carrying antizyme 4 behind the yeast GPD1 promoter). Liquid cultures were grown overnight in selective polyamine-free glucose medium. The overnight culture was adjusted to A600 3.0/ml and serial dilutions were spotted (2 μl of aliquots) as indicated on polyamine-free selective galactose plates. The plates were then incubated for 3 days at 30 °C. The results shown are representative for multiple experiments.