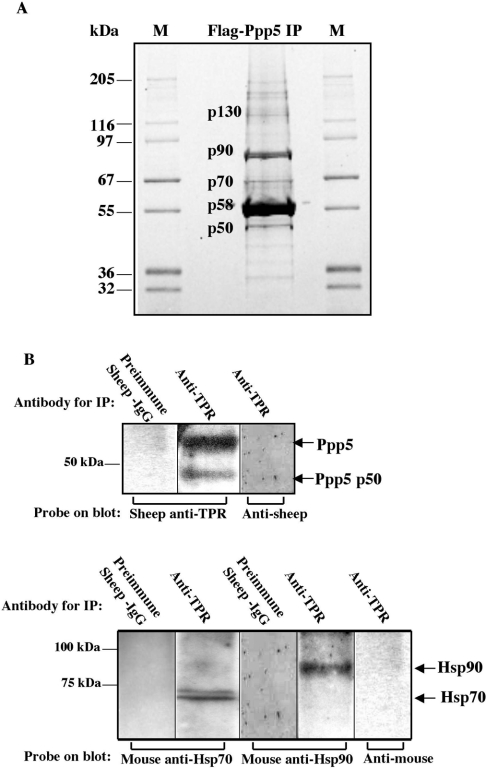
Figure 1. Detection of proteins interacting with Ppp5.
(A) Proteins bound to FLAG–Ppp5 were separated by SDS/PAGE and stained with Sypro Orange. Vector expressing FLAG–Ppp5 was transfected into HEK-293 cells. Lysates were incubated with anti-FLAG–agarose, and the adsorbed material was eluted with FLAG peptide from a column of the anti-FLAG–agarose. Proteins in the eluate were separated by SDS/PAGE, excised from the gel and digested with trypsin. Their peptides were analysed using MS, followed by identification of the proteins using the UCSF Protein Prospector database (http://prospector.ucsf.edu/). Bands providing sufficient material for identification by protein fingerprinting are labelled: p50, Ppp5 truncated at C-terminus; p58, FLAG–Ppp5; p70, Hsp70; p90, Hsp90; p130, high-molecular-mass form of Ppp5. M lanes, marker proteins of the indicated molecular masses in kDa. (B) Detection of Hsp70 and Hsp90 in anti-TPR immunopellets. Antibodies against the TPR-domain of Ppp5 coupled to Protein-G–Sepharose or control antibodies coupled to Protein-G–Sepharose were incubated with lysates from HEK-293 cells. Following centrifugation, proteins in the pellet were analysed by SDS/PAGE and subsequent immunoblotting with anti-Hsp70, anti-Hsp90 or anti-TPR antibody, followed by appropriate secondary antibodies and detection by ECL®. Note that the buffer systems in (A) and (B) are different. Ppp5 p50 in (B) migrates at the same position as p50 in (A) when the same buffer system is used.