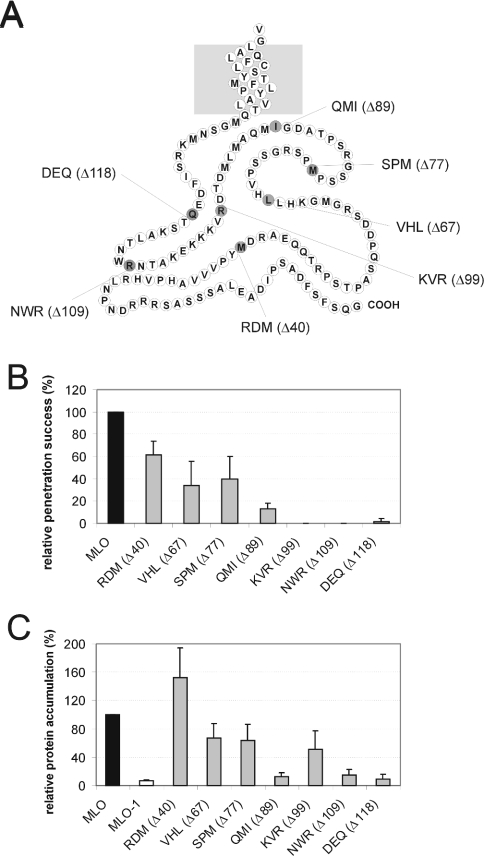
Figure 4. Integrity of the C-terminus is critical for MLO functionality.
(A) Schematic representation of the MLO C-terminus and indication of the derived C-terminal truncation variants. The light-grey box symbolizes the lipid bilayer. Individual amino acids are shown as circles labelled using the one-letter amino acid code. The last amino acid of the respective indicated constructs carrying C-terminal truncations is highlighted in dark grey. (B) Functional assay of MLO variants. Leaf segments of the powdery-mildew-resistant barley cultivar BC Ingrid mlo-5 were bombarded with the bifunctional plasmid pUGLUM (encoding the GFP reporter plus wild-type MLO) or a mutant version thereof [encoding GFP plus either RDM (Δ40), VHL (Δ67), SPM (Δ77), QMI (Δ89), KVR (Δ99), NWR (Δ109) or DEQ (Δ118)]. Leaves were then inoculated with Bgh A6 and GFP-fluorescent cells were inspected for fungal structures as described in the Materials and methods section. (C) Assessment of MLO protein accumulation. Relative accumulation of wild-type MLO, mutant version MLO-1, as well as variants RDM (Δ40), VHL (Δ67), SPM (Δ77), QMI (Δ89), KVR (Δ99), NWR (Δ109) and DEQ (Δ118) carrying increasing C-terminal truncations was determined by dual-luciferase assays of transfected A. thaliana protoplasts as described in the Materials and methods section.