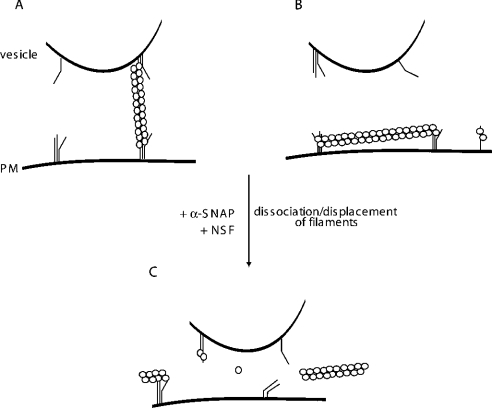
Figure 7. Models for Sept5 organization and role in secretion.
(A) Septins may act as molecular tethers. By binding to 7 S complexes both on the vesicle and the plasma membrane, Sept5 and associated septins (○○) can physically restrict the movement of vesicles towards the membrane. (B) Septins may create a physical barrier to the membrane. Alternatively, septins may form networks parallel to the membrane demarcating inactive zones where SNAREs are incompetent for fusion. (C) α-SNAP displaces the septins. In either scenario, α-SNAP can then displace Sept5 from the 7 S complex, priming the SNAREs for fusion. The formation of trans complexes would then lead to exocytosis.