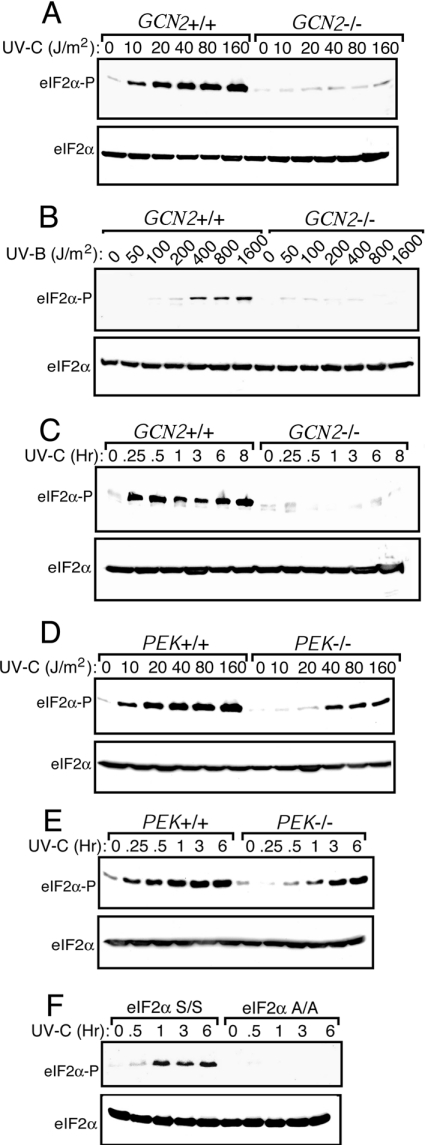
Figure 1. Phosphorylation of eIF2α by GCN2 is enhanced in response to UV irradiation.
GCN2+/+ and GCN2−/− MEF cells were subjected to increasing dosages of UV-C (A) or UV-B irradiation (B). After UV treatment, cells were incubated in the culture medium for 3 h and the levels of phosphorylation of eIF2α were measured by immunoblot by using a polyclonal antibody specific to eIF2α phosphorylated at Ser51. Equal amounts of proteins were analysed in each lane. Levels of total eIF2α were assayed by using an antibody that recognizes both phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated versions of the translation initiation factor. GCN2+/+ and GCN2−/− (C) or PEK+/+ and PEK−/− (E) MEF cells were subjected to 30 J/m2 UV-C irradiation, incubated in the culture medium for between 0.25 and 8 h as indicated, and eIF2α phosphorylation was measured by immunoblot. (D) PEK+/+ and PEK−/− MEF cells were subjected to increasing dosages of UV-C, cultured for 3 h, and the amounts of eIF2α phosphorylation were measured by immunoblot. (F) S/S and A/A MEF cells were exposed to 30 J/m2 UV-C irradiation, and after between 0.5 and 6 h incubation as indicated, phosphorylated eIF2α and total eIF2α levels were measured by immunoblot. Immunoblots in each panel are representative of three independent experiments.