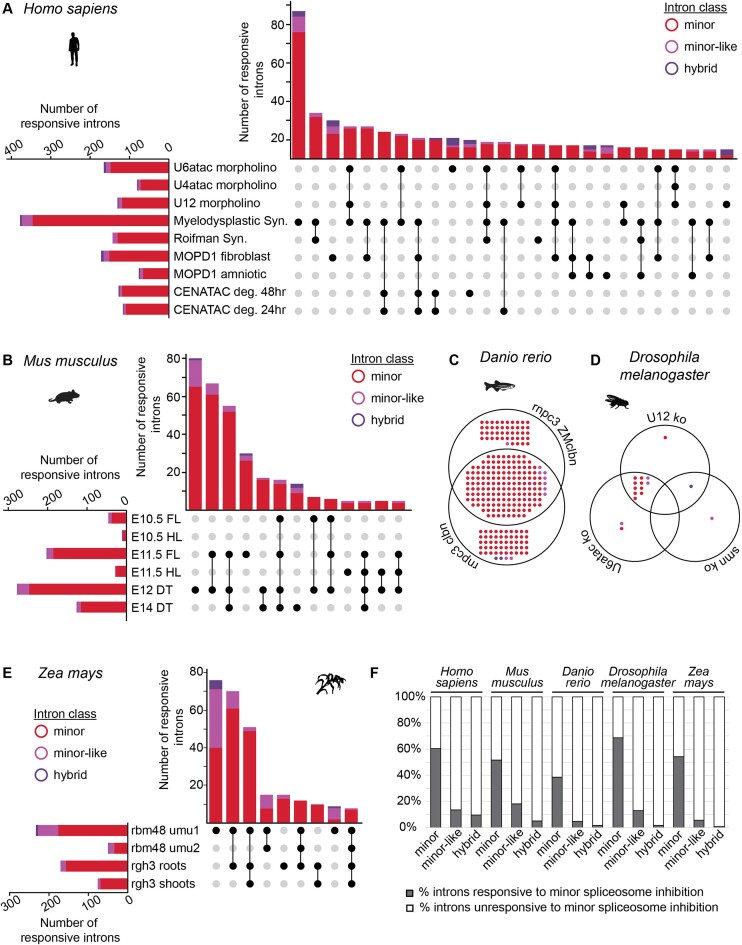
Figure 5.
Identification of introns responsive to minor spliceosome inhibition. (A, B) Upset plot for mis-spliced introns in different (A) human and (B) mouse datasets in which the minor spliceosome is inhibited. Intersections with fewer than five introns have been omitted. (C, D) Venn diagram for mis-spliced introns in different (C) zebrafish and (D) fruit fly datasets in which the minor spliceosome is inhibited. (E) Upset plot for mis-spliced introns in different maize datasets in which the minor spliceosome is inhibited. Intersections with fewer than five introns have been omitted. Color-coding for intron classes in Figure 5 is the same as in Figure 1. Significant retention and/or alternative splicing of introns was identified using a one-tailed Welch's t-test. Responsive introns were defined as those found in genes expressed above 1 TPM, with a significantly increased mis-splicing index (P< 0.05) in minor spliceosome loss-of-function conditions. (F) Bar graphs with total number of responsive minor, minor-like and hybrid introns in the different model organisms. For more information on the analyzed RNAseq datasets (including experimental conditions and N-value), see also Supplementary Table S3. See also Supplementary Figure S12-S18 and Supplementary Table S6. Deg = degron; syn = syndrome; FL = forelimb; HL = hindlimb; DT = dorsal telencephalon.