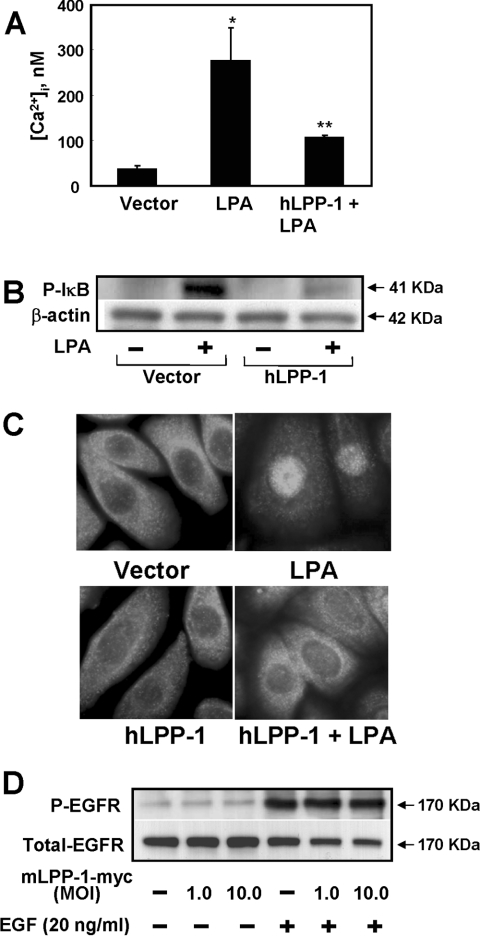
Figure 4. Effects of overexpression of hLPP-1 on LPA-induced changes in [Ca2+]i, IκB phosphorylation, NF-κB translocation and EGF-R phosphorylation.
HBEpCs (∼70% confluence) on coverslips were infected with vector control or hLPP-1 wt adenoviral construct (MOI 25) for 48 h. (A) Cells were loaded with the fluorescent calcium indicator fura 2 acetoxymethyl ester (5 μM) for 15 min and then challenged with 1 μM LPA for 10 min. [Ca2+]i was measured as the ratio of 340/380 nm fluorescence and expressed as nM. *P<0.05 compared with vector control; **P<0.05 compared with LPA treatment. (B) Cells were challenged with 1 μM LPA for 10 min, and total cell lysates were subjected to SDS/PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against phospho-IκB and IκB. Equal loading was confirmed by blotting for β-actin. Shown is a representative blot of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (C) Cells were challenged with medium containing or not 1 μM LPA for 15 min and subjected to immunostaining with antibody against NF-κB subunit (p65) and examined by fluorescent microscopy. Each immunofluorescent image is representative of three different experiments. (D) HBEpCs (∼70% confluence in 35 mm dishes) were infected with vector or with Myc-tagged mLPP-1 wt adenoviral construct (MOI 1–10) for 24 h. Cells were challenged with medium alone or medium containing EGF (20 ng/ml) for 15 min. Cell lysates were prepared as described above and subjected to SDS/PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against phospho-EGF-R (Y1173) and EGF-R. Each Western blot is representative of two independent experiments.