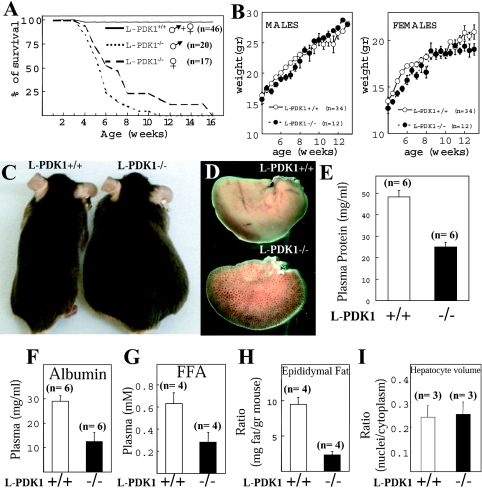
Figure 2. Survival and characterization of liver failure in L-PDK1−/− mice.
(A) The indicated number of male and female mice were maintained under standard husbandry conditions and the percentage of surviving mice of each age is indicated. (B) The body masses (in g) of male and female L-PDK1+/+ and L-PDK1−/− mice at the indicated age are represented. Values represent the means±S.E.M. for each data point, with the number (n) of mice shown. (C) Photograph of the indicated littermate mice showing the interstitial oedema in the L-PDK1−/− mice before death. (D) Representative right hepatic lobe from L-PDK1+/+ and L-PDK1−/− mice of 7 weeks of age. Total plasma protein (E), albumin (F) and FFAs (G) were measured in the indicated mice. (H) The mass of the peri-epididymal fat pad is represented as a ratio of the total mass of the mouse. (I) The hepatocyte volume was estimated using the unbiased dissector principle and represented as nuclei/cytoplasm ratio, as there is no difference in nuclear volume between L-PDK1+/+ and L-PDK1−/− hepatocytes (results not shown). In (E)–(I), the data are presented as the means±S.D., with the number (n) of animals employed shown.