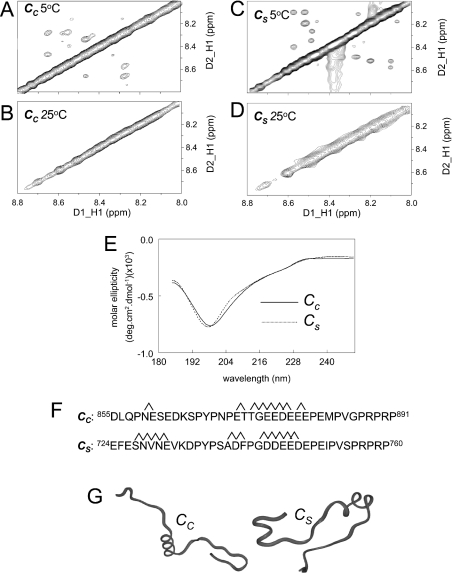
Figure 8. Comparison of structures of Cc and Cs.
(A)–(D) The amide–amide region of the Cc and Cs NOESY spectra respectively in 10% 2H2O/90% H2O, at 5 °C (A and C) or 25 °C (B and D). The off-diagonal cross-peaks in the 5 °C spectrum are indicative of helical structure, whereas the lack of cross-peaks at 25 °C indicate random coil structures. (E) CD spectra for Cc and Cs at 25 °C show a minima at approx. 200 nm, suggesting a mixture of random coil and helical structure. Assignment of the connectivities contributing to the NOE (nuclear Overhauser effect) cross-peaks at 25 °C indicated helical structure between residues as indicated in (F), allowing prediction of the structures in (G). In Cc, there is a helical turn involving residues 5 and 6, helical structure between residues 17 and 26. In Cs, there is helical structure between residues 4 and 8, and between residues 16 and 25.