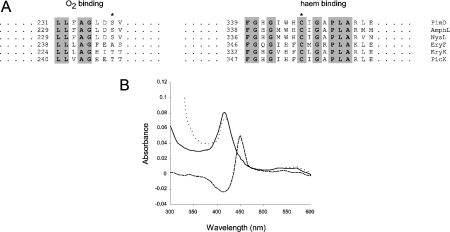
Figure 2. Identification of PimD as an authentic cytochrome P450.
(A) Comparison of O2-binding pockets and haem-binding sequences from some macrolide P450 mono-oxygenases. The asterisk on the left alignment shows the conserved threonine/serine (alanine in EryF) residues that are believed to be involved in O2 scission, whereas the asterisk on the right indicates the haem-binding cysteine residue. Conserved amino acids are shown in bold and are highlighted. Numbers indicate amino acid residues from the N-terminus of the protein. AmphL, St. nodosus P450 involved in amphotericin biosynthesis (GenBank® accession number AAK73504); NysL, St. noursei P450 involved in nystatin biosynthesis (GenBank® accession number AAF71769); EryF (GenBank® accession number Q00441) and EryK (GenBank® accession number P48635), P450s from Sa. erythraea involved in erythromycin biosynthesis; PicK, methymycin/picromycin hydroxylase from St. venezuelae (GenBank® accession number AAC64105). (B) CO difference spectrum of purified PimD. The continuous line indicates the absorbance spectrum of the pure protein in storage buffer. The dotted line denotes the spectrum of the protein reduced with Na2S2O4. The reduced CO-difference spectrum is indicated by a broken line.