Figure 1.
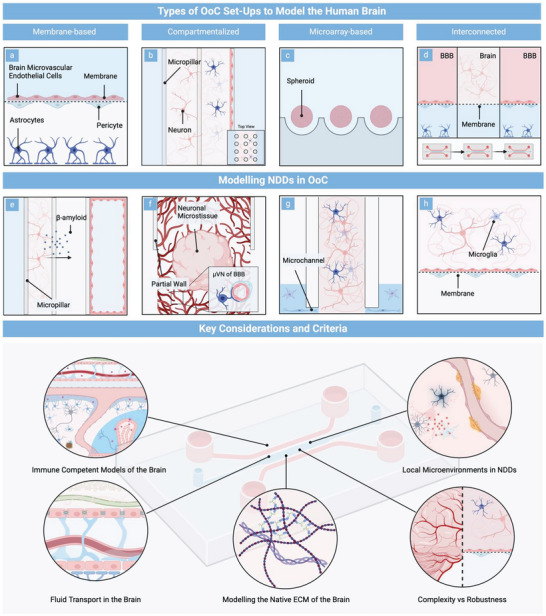
Top panel: Schematic representation of the cross‐sectional areas of the four different types of microfluidic setups employed in modeling the human brain, including a) membrane‐based, b) compartmentalized, c) microarray‐based, and d) interconnected platforms. Schematic representation of the cross‐sectional areas of critical MPS setups that have been employed to model NDDs in vitro, including e) a compartmentalized platform to model the effect of aβ on an endothelial lumen, f) a neurovascular co‐culture model interconnecting aβ overexpressing neurospheres with a self‐assembled network of the BBB, g) a compartmentalized AD platform for emulating microglial recruitment, and (h) a membrane‐based model to study vascular dysfunction in the context of PD. Bottom panel: Graphical representation of the key considerations and criteria MPS developers need to address prior to advancing microphysiological NDD models.
