Figure 7.
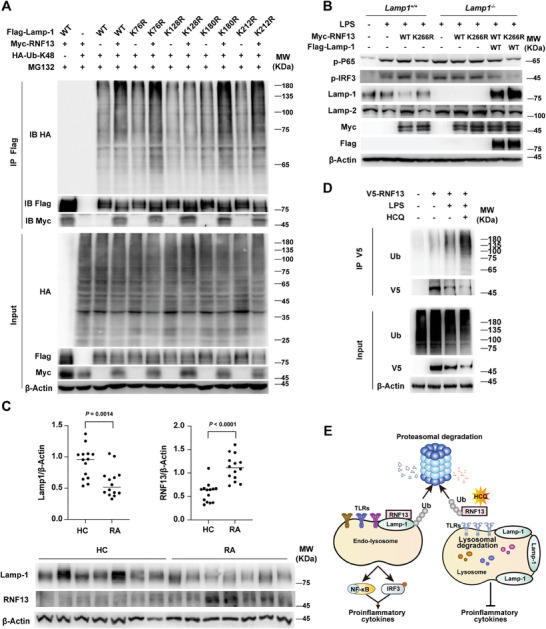
RNF13 induces LAMP‐1 degradation by mediating K48‐linked polyubiquitination on its K128 position and is involved in RA pathogenesis. A) Co‐immunoprecipitation analysis of K48‐linked polyubiquitination mediated by RNF13 on different LAMP‐1 point mutants in HEK293T cells transfected with RNF13, K48 ubiquitin (Ub) and different point mutants of LAMP‐1, and treated with MG132 (3 µM) for 5 h. B) Western blot assay of RNF13 (WT and K266R) and LAMP‐1′s effect on TLR4 signaling pathway in Lamp1 +/+, Lamp1 −/− RAW264.7 cells and Lamp1 −/− RAW264.7 cells overexpressed by LAMP‐1, transfected with WT or K266R of RNF13 and treated with or without LPS (100 ng mL−1) for 3 h. C) Relative intensity of RNF13 and LAMP‐1 in PBMCs from HC and RA patients that is calculated by the ImageJ program (Up). Western blot analysis of RNF13 and LAMP‐1 in PBMCs from HC and RA patients (Down). D) Co‐immunoprecipitation analysis of hydroxychloroquine's (HCQ) effect on polyubiquitination of RNF13 in THP‐1 cells transfected with V5‐RNF13 or not and treated with LPS (100 ng mL−1) for 3 h or not. E) Proposed working model for RNF13 as a positive regulator of endosomal TLRs‐mediated inflammatory response by targeting LAMP‐1 for K48‐linked polyubiquitination and degradation. Data are representative of three independent experiments (A, B, D) or shown as mean ± SD of n = 14 biological replicates (C), two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test (C).
