Fig. ED8: SIN3b binds Myt1l via N-terminal SID domains and is essential for reprogramming.
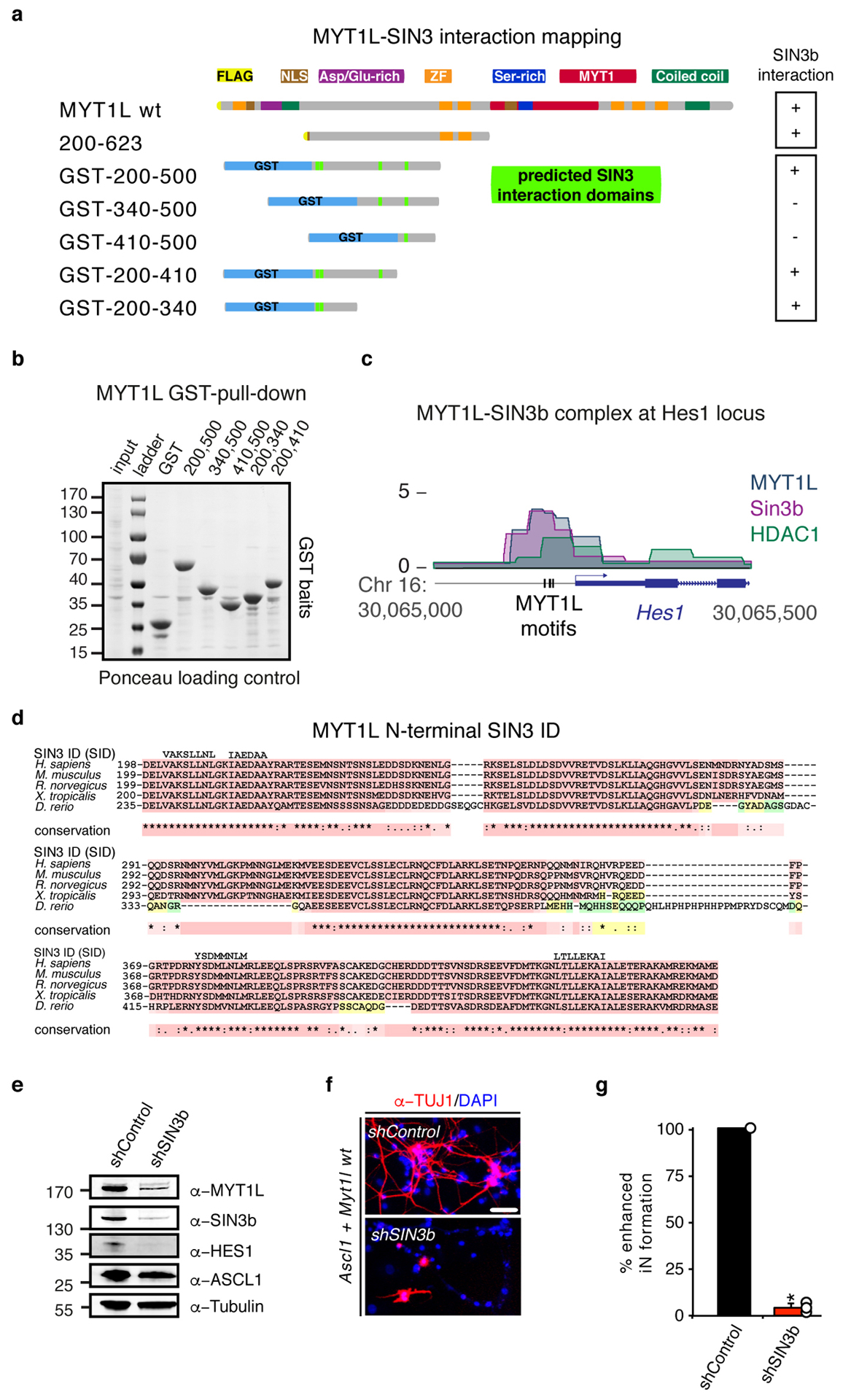
a, Schematic of FLAG and NLS-tagged Myt1l truncations and glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged Myt1l fusion proteins, highlighted are putative SIN3 interactions domains (SID)(See also Fig. 3). Ability to biochemically interact with SIN3b is indicated by (+) and (−), respectively. b, GST bait loading after pull down was controlled by Ponceau staining of the Western blot membrane. Input = 0.2% of pull down (PD) input, PD lanes = 20% of PD eluates. c, ChIP-seq tracks of SIN3b, HDAC1, and Myt1l shows binding at the Hes1 promoter two days after MEF reprogramming with Ascl1, Brn2, and Myt1l wt. Vertical bars mark Myt1l AAGTT-motifs. d, Multiple sequence alignments of the highly conserved putative SIN3 interaction domains (SID) within minimal functional region of Myt1l from selected eukaryotic species. The alignment was generated using T-Coffee and putative SID regions are shown above the alignment. e, Western blot of iN cells derived from MEFs upon reprogramming for 2 days with Ascl1, Myt1l wt together with either control or Sin3b-targeting shRNA constructs using indicated antibodies. f, Representative micrographs of iN cells derived in D upon reprogramming for 14 days followed by immunofluorescence using antibodies against TUJ1 (red) and DAPI staining (blue), scale bar 50 μm. g, Conversion efficiency of cells shown in D based on TUJ1-positive cells with neuronal morphology highlight the deleterious effect of Sin3b knock-down on iN formation. n = 3, error bars = SE, t-test * p < 0.005.
