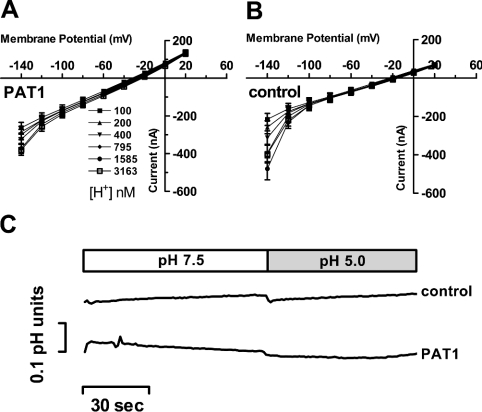
Figure 4. Recordings of I–V relationships and intracellular pH changes in oocytes expressing PAT1 in the absence of amino acid substrates.
(A and B) Inward currents recorded in oocytes expressing PAT1 (A) or water (B) injected controls were perfused with Na+-free buffer solutions of six different pH values (pH 7.0–5.5). Oocytes were clamped to −40 mV, and I–V relationships were recorded in the potential range between +20 mV and −140 mV. At the end of the experiment, oocytes expressing PAT1 were perfused with 20 mM GABA at pH 5.5 and inward currents of 900±89 nA were obtained, demonstrating the functional PAT1 expression level. No significant changes in the reversal potential could be determined between water-injected and PAT-expressing oocytes upon alterations in pHout and membrane voltage. Data represent the means±S.E.M. for at least eight oocytes in each experiment. (C) Representative intracellular pH changes (ΔpH) in oocytes injected with water or PAT1 cRNA and perfused with buffer pH 7.5 or pH 5.0 in the absence of substrate. Oocytes were clamped to −40 mV and intracellular pH, as well as holding currents, were recorded (holding currents are not shown). As a control, at the end of the experiment, the functional PAT1 expression level was determined by measuring the current and ΔpH induced by 20 mM glycine at pH 5.0 (current 1704±169 nA; ΔpH 0.57±0.15; n=3).