Fig. 4:
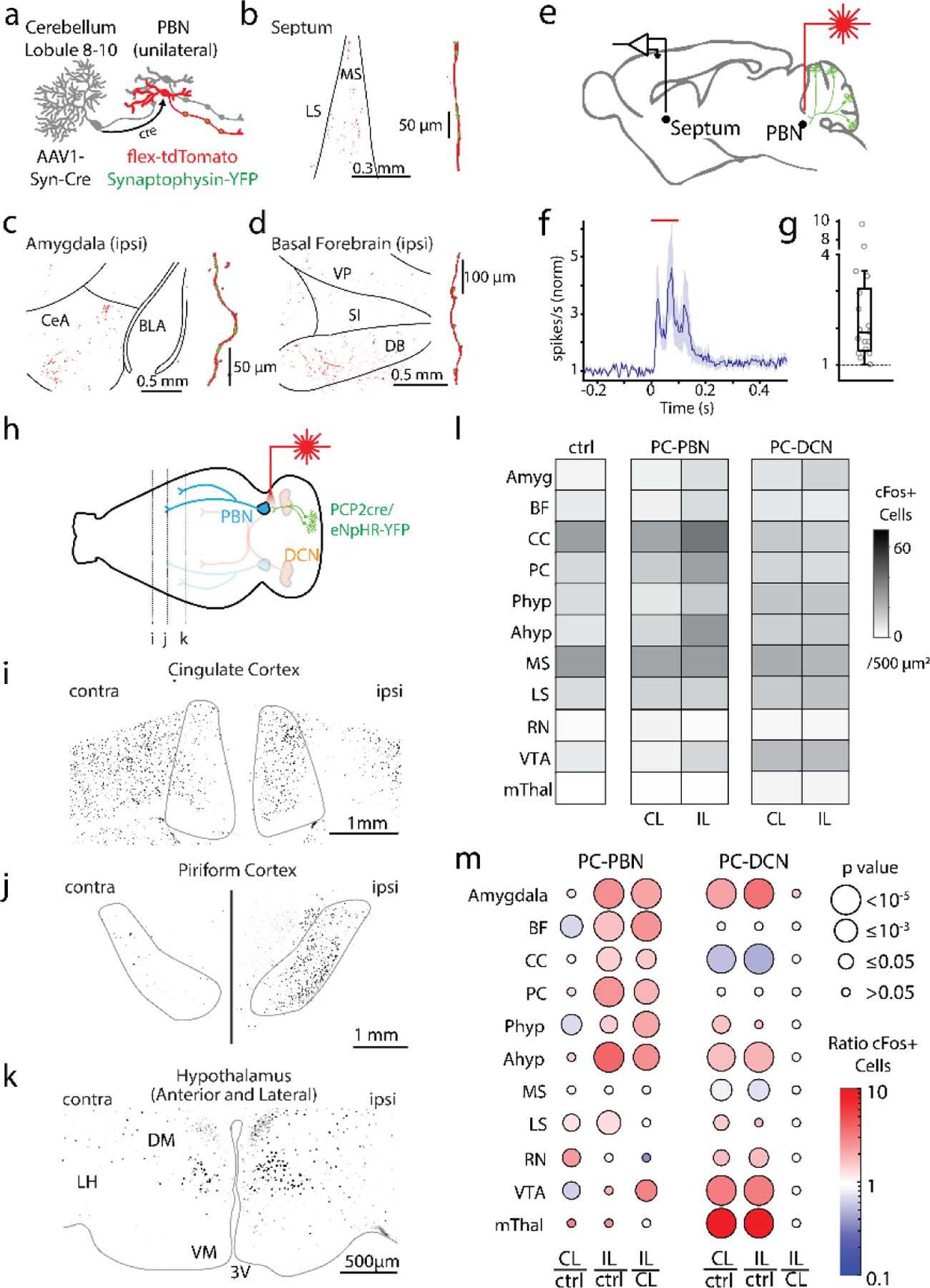
Purkinje cell-recipient PBN neurons project to and influence numerous forebrain brain regions
a. Injections of anterograde AAV-cre into the posterior vermis and AAVs with flex-tdTomato and synaptophysin-YFP and into the PBN, labelled PC-recipient PBN neurons with tdT and the presynaptic boutons of all PBN neurons with YFP.
b. left, Low magnification fluorescence image of the septum. right, high magnification image of a reconstructed axon (red) in the septum and colocalized synaptophysin-YFP (green).
c. Same as b, but for the amygdala.
d. Same as c, but for the basal forebrain.
e. Optical suppression (100 ms in Halo/PCP2-Cre mice) of the PC-PBN pathway elevates firing in the septum.
f. Average response (n=17 cells). Shaded area indicates standard error.
g. Distribution of normalized responses due to optical suppression of the PC-PBN pathway
h. Schematic. Following unilateral optical suppression of either the PC-PBN or PC-DCN pathway, slices were stained for c-Fos.
i-k. c-Fos staining for the coronal slices indicated in h.
l. Quantification of c-Fos expression after ipsilateral (IL) PC-PBN, PC-DCN, or control (wildtype) stimulation.
m. The ratio of c-Fos expression in the stimulated (IL) and unstimulated (CL) hemisphere was determined relative to control (ctrl) mice. The ratio IL to CL expression was also determined. The average ratio (color) and the statistical significance (symbol size) are indicated (Table 1). BF: Basal forebrain, CC: Cingulate Cortex, PC: Piriform Cortex, Phyp: Hypothalamus Preoptic Area. Ahyp: Hypothalamus Anterior and Lateral (as in k), MS: Medial Septum, LS: Lateral Septum, RN: Red Nucleus, VTA: Ventral Tegmental Area, mThal: Motor thalamus.
