Fig. 5.
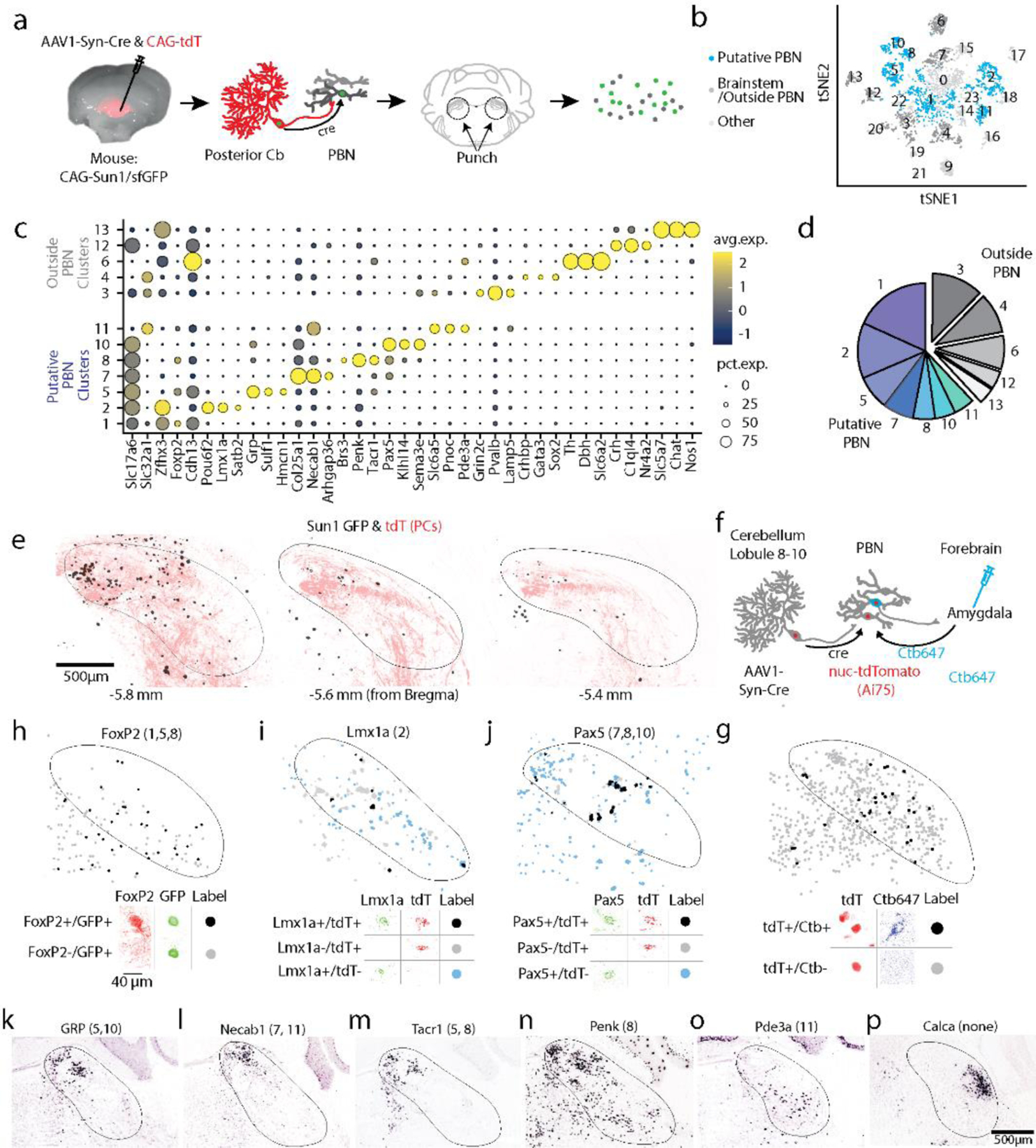
Diversity of PBN neurons directly targeted by PCs.
a. Schematic showing the strategy used to label PC targets. AAV1-Syn-Cre was injected into the posterior vermis of a CAG-Sun1/sfGFP mouse. The nuclei of target PBN neurons were trans-synaptically labelled and sorted.
b. tSNE visualization of 3876 neuronal nuclei separated into 23 neuronal clusters (Extended Data Fig. 10)
c. Dot plot of scaled expression for indicated clusters. Clusters with cerebellar markers, unclustered nuclei, and clusters of < 100 nuclei were removed (Extended Data Fig. 10)
d. Fraction of labelled nuclei per cluster.
e. Labelling of nuclei (black) and PC axons (red) in 3 coronal planes following an injection as in a, along with a AAV1-CAG-tdTomato coinjection.
f. Schematic showing the strategy used to retrogradely label cells projecting to the amygdala and anterogradely label PBN neurons directly inhibited by PCs.
g. (top) A fraction of TdT + neurons were retrogradely labelled by cholera toxin injected into the amygdala (black) and many were not (grey). (bottom) Representative cells showing labelling and the corresponding symbols used to present cell locations.
h. (top) A fraction of trans-synaptically labelled PBN neurons were Foxp2+ (black) and many were Foxp2- (grey). (bottom) Representative cells showing Foxp2 immunohistochemistry and nuclear labeling.
i. In situ hybridization for Lmx1a and tdTomato labelled a fraction of the trans-synaptically labelled cells (black) in a tdTomato reporter mouse (Ai75d). Labelled cells were often found in groups of 3–4 cells.
j. Same as (g) but for Pax5.
k-p. Images from the Allen Brain Atlas staining for selected genes corresponding to indicated clusters. Calca labels CGRP neurons in the PBN that were not trans-synaptically labelled.
