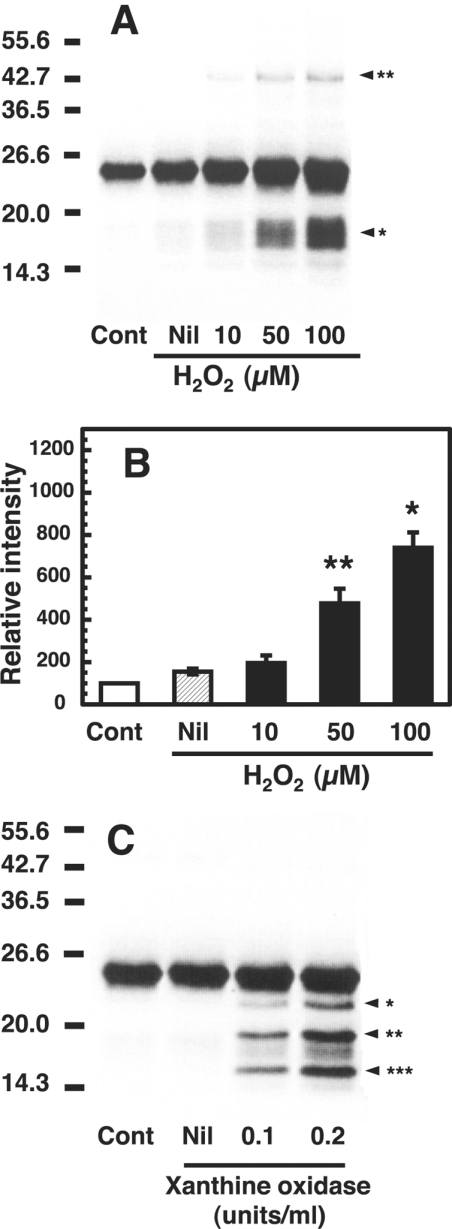
Figure 4. Fragmentation and dimerization of the copper-loaded PrP23–231 in the presence of H2O2 and O2−.
(A) Western blot immunoassay of copper-loaded PrP23–231 treated with H2O2. Mixtures containing 50 mM Mes (pH 7.5) and 1 μM copper-loaded PrP23–231 (containing 5.0 μM copper) were incubated without (Nil) or with the indicated concentrations of H2O2 at 37 °C for 30 min. Copper-loaded PrP23–231 without the incubation was used as a control (Cont). PrP was detected by SDS/PAGE followed by immunoblotting with antibody SAF 84. Molecular masses in kDa are indicated on the left. The positions of the fragments at 17–19 kDa and the dimer at 46 kDa are marked by arrowhead* and arrowhead** respectively. (B) Quantification of the Western blot data. Signals of the 17–19 kDa fragments were determined using ATTO Densitograph Software Library and plotted as a percentage of the control (zero time, Cont). Data are means±S.D. (n=3). Significant difference (*P≤0.01 and **P≤0.05) from the experiment with no additions (Nil). (C) Western blot immunoassay of copper-loaded PrP23–231 treated with O2−. Mixtures containing 50 mM Mes (pH 7.5), 0.1 mM xanthine and 1 μM copper-loaded PrP23–231 (containing 5.0 μM copper) were incubated without (Nil) or with the indicated concentrations of xanthine oxidase at 37 °C for 30 min. As a control, copper-loaded PrP23–231 was incubated without xanthine (Cont). PrP was detected by SDS/PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with antibody SAF 84. Molecular masses in kDa are indicated on the left.