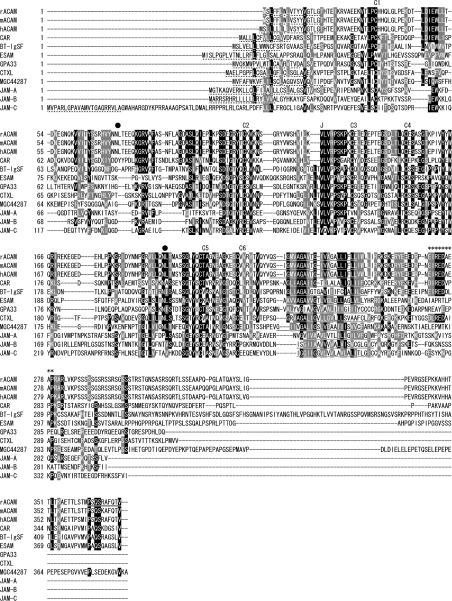
Figure 2. Amino acid sequences of rat, mouse, and human ACAM and sequence alignment with other CTX family members in human.
Multiple sequence alignment was performed by Clustal W, using amino acid sequences of rat ACAM (rACAM; GenBank® accession number, AF302047), mouse ACAM (mACAM; AY326421), human ACAM (hACAM; AY326422), CAR (Hs.473417), BT-IgSF (Hs.112873), ESAM (Hs.173840), CTXL (Hs.112377), MGC44287 (Hs.177164), GPA33 (Hs.437229), JAM-A (Hs.414880), JAM-B (Hs.436494) and JAM-C (Hs.419149). Identical and similar amino acids are boxed in black and grey respectively. Signal sequences are indicated by broken lines. Transmembrane segments are underlined. Rabbit polyclonal serum was raised against a synthetic peptide at the C-terminal end (bold and underlined). N-glycosylation sites are indicated by closed circles. ACAM, CAR, BT-IgSF and CTXL share the motif D/EI/LREDXXXP (indicated by asterisks). The six cysteine residues, C1 to C6, forming disulphide bonds in V- and C2-type Ig domains, are indicated. The J-segment motif (VLV) is indicated by J.