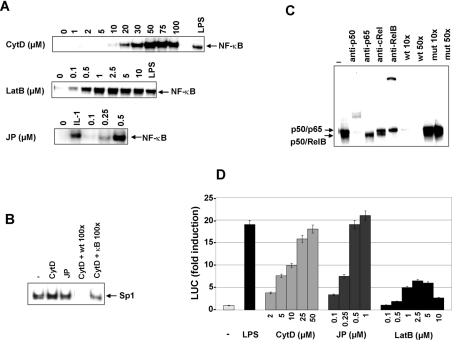
Figure 2. Actin dynamics modulation by CytD, LatB and JP induces an activation of NF-κB in myelomonocytic cell lines.
(A) NF-κB nuclear translocation in response to actin cytoskeleton disruption by CytD, LatB and JP. Myelomonocytic cell lines were either treated or not with LPS (10 μg/ml), IL-1β (100 units/ml) or various concentrations of CytD (U937 cells), LatB (HL-60) or JP (THP-1) for 150 min. The DNA-binding activities in nuclear extracts were analysed by EMSA with a consensus binding site for NF-κB. (B) Nuclear proteins of CytD-treated cells (50 μM) or JP-treated cells (0.5 μM) were analysed by EMSA with a specific Sp1 probe. Competition experiments were performed with an excess of unlabelled oligonucleotide carrying the consensus site for Sp1 (CytD+wt, 100×) or NF-κB (CytD+κB, 100×). (C) Identification of NF-κB complexes. Supershift and competition assays were performed on nuclear extracts of U937 cells treated by CytD (50 μM) for 150 min. Nuclear proteins were incubated with antibodies specific for p50, p65, RelB and c-Rel or with an excess (10- or 50-fold) of unlabelled oligonucleotide wild-type (wt) or mutated (mut) before being analysed by EMSA with a consensus NF-κB binding site. (D) Actin cytoskeleton disruption by CytD, LatB and JP induces NF-κB-mediated transcription. HL-60 cells, 24 h post-transfection with a (κB)5LUC reporter plasmid, were either treated or not with LPS (10 μg/ml) or various concentrations of CytD, JP or LatB for 6 h before being harvested for LUC assays. Values are presented as means±S.D. (n=3).