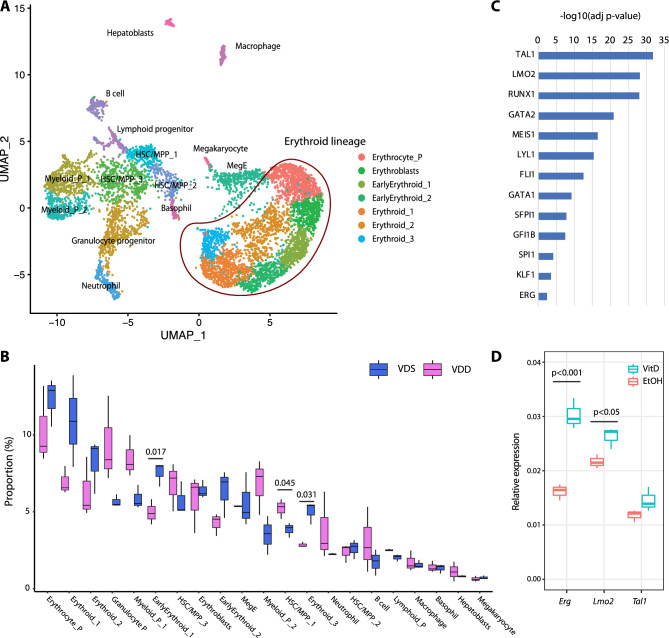
Fig. 5.
Prenatal vitamin D deficiency alters cellular compositions of the embryonic liver, suggesting immune cell proportion changes start during development. (a) UMAP representation of single-cell RNA-seq gene expression data and cellular lineage identification of E14.5 fetal liver (n = 3 per group). (b) The boxplots indicate prenatal vitamin D deficiency alters cellular compositions of E14.5 fetal liver. (c) Genes downregulated in VDD E14.5 fetal liver are enriched in the genes regulated by hematopoietic transcription factors. (d) Treating HPC7 cells with 1-alpha-25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 significantly increases gene expression levels of Erg and Lmo2, suggesting these genes are regulated by VDR (n = 3 per treatment group).