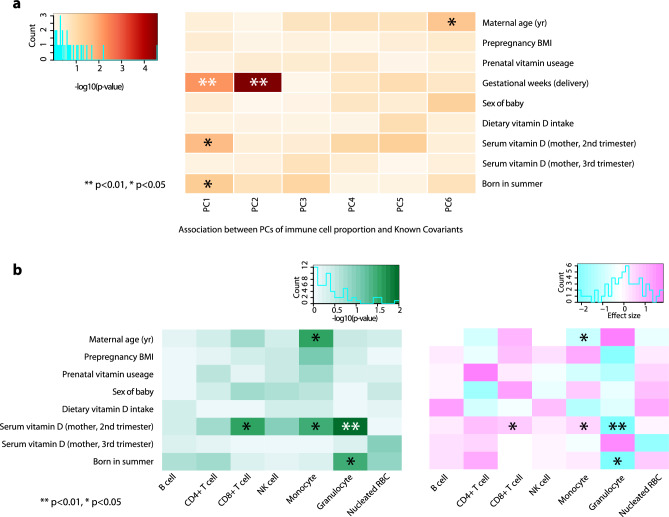
Fig. 6.
Maternal serum vitamin D status in the second trimester is positively associated with the CD8+ T cell proportion in the cord blood. (a) The heatmap shows that the gestational week at the delivery has the strongest associations with immune cell composition variations assessed by the principal component (PC), followed by maternal serum vitamin D (2nd trimester) and being born in the summer season. (b) After adjusting for the sex of the fetus, gestational age, the season of T1, and the gestational week at T1, maternal serum vitamin D (2nd trimester) maintains significant associations with immune cell composition, specifically positive association with proportions of CD8+ T cell and monocytes, and negative association with granulocytes. Asterisks indicate the significance (**p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test). The left panel shows − log10(p-value), and the right panel shows the direction of the associations.