FIGURE 5.
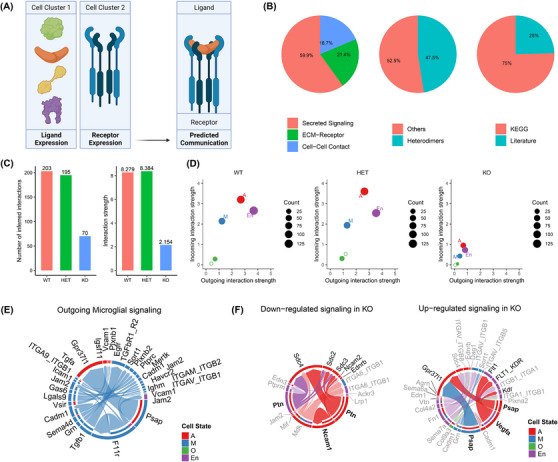
Total loss of Inpp5d significantly reduces global signaling between cell types in female mice but increases proastrocytic signaling between microglia and astrocytes. (A) CellChat uses the expression of 2021 ligands and receptors between pairs of cells in scRNAseq data sets to infer cell–cell communication. (B) Characteristics of ligand–receptor interactions in the CellChat database. (C) The number and strength of inferred interactions drops substantially on homozygous loss of Inpp5d in female mice. (D) Numbers and strengths of incoming and outgoing interactions decrease in all cell types on total loss of Inpp5d in female mice. (E) Outgoing microglial signaling pathways in all female mice. Most signals occur between microglial and astrocytes or other microglia. (F) Chord plots showing pathways with decreased and increased signaling in Inpp5d −/− mice compared to wild‐type. Plot circumference shows outgoing signaling from cell type (outer band) to recipient cell type (inner band). Width of outer bands represents numbers of cells per pathway. All pathways shown are significantly dysregulated; some bands are emphasized for the purpose of visualization.
