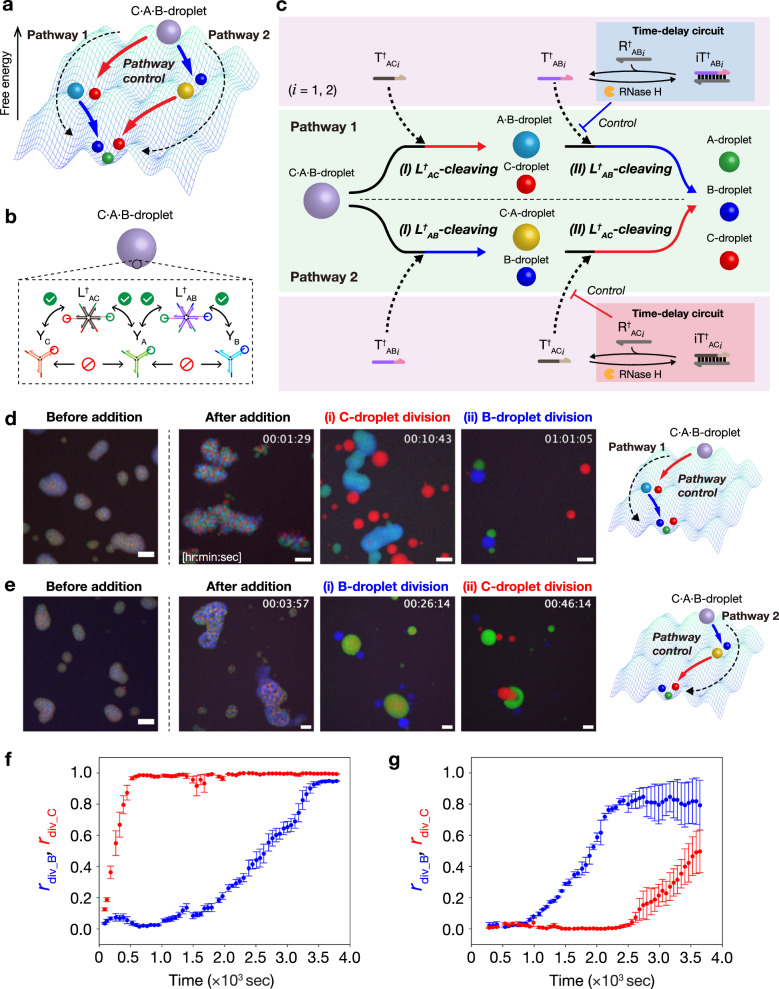
Fig. 5. Control of droplet division pathway.
a A reaction landscape of the division of ternary-mixed DNA droplets. The division pathway indicates the order of droplet division. b Formation of ternary-mixed DNA droplet (C·A·B-droplet) containing three types of Y-shaped DNA nanostructures and two types of DNA linkers. c Schematic of pathway-controlled division of C·A·B-droplet. The linker-cleavage reaction rates decide the order of droplet division, thereby changing the pathway of droplet division. d Time-lapse images of C·A·B-droplet division in Pathway 1 before and after adding T†ACi, iT†ABi, R†ABi, and RNase H. The detail of multistep division process is shown in Supplementary Movie 6. R†ABi (i = 1, 2): miR-6875-5p and miR-4634. Scale bars: 20 μm. e Time-lapse images of C·A·B-droplet division in Pathway 2 before and after adding T†ABi, iT†ACi, R†ACi, and RNase H. The detail of multistep division process is shown in Supplementary Movie 7. R†ACi (i = 1,2): miR-1246 and miR-1307-3p. Scale bars: 20 μm. f, g Time courses of division ratio rdiv_B (blue) and rdiv_C (red) during C·A·B-droplet division in Pathway 1 (f) and Pathway 2 (g), respectively. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error (SE) of three field of view of microscopy observation.