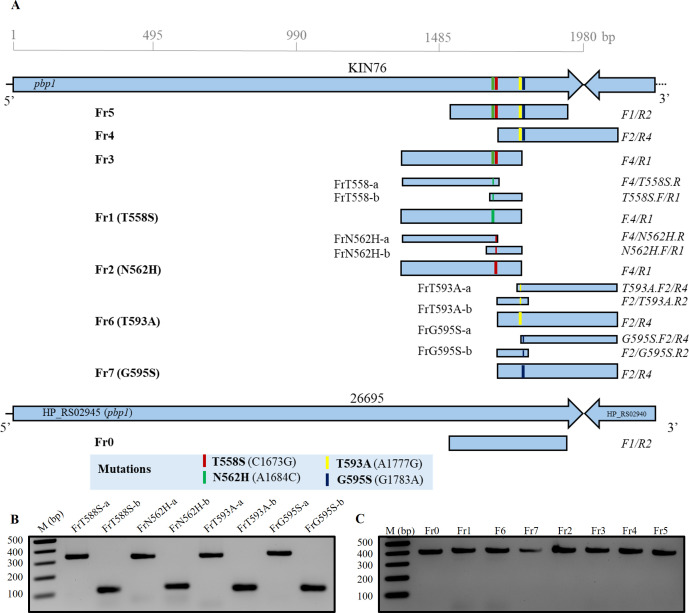
Fig 1.
Amplicon construction. The pbp1 DNA fragments carrying different rearrangements of mutations were amplified by PCR from genomic DNA of clinical isolate KIN76 (A). Amplicons Fr1, Fr2, Fr6, and Fr7 carrying a single mutation were additionally constructed by fusion PCR of the single-stranded DNA fragments FrT558S-a/FrT558S-b, Fr2a/Frb2, FrT593A-a/FrT593A-b, and G595S-a/G595S-b, respectively. A DNA fragment (Fr0) without any mutation was also prepared from 26695 genomic DNA and used as a negative control. The PCR fragments before fusion PCR (B). All the final KIN76 amplicons prepared before transformation into strain 26695 (C). All the PCR fragments were checked in 1.8% agarose S gel electrophoresis.