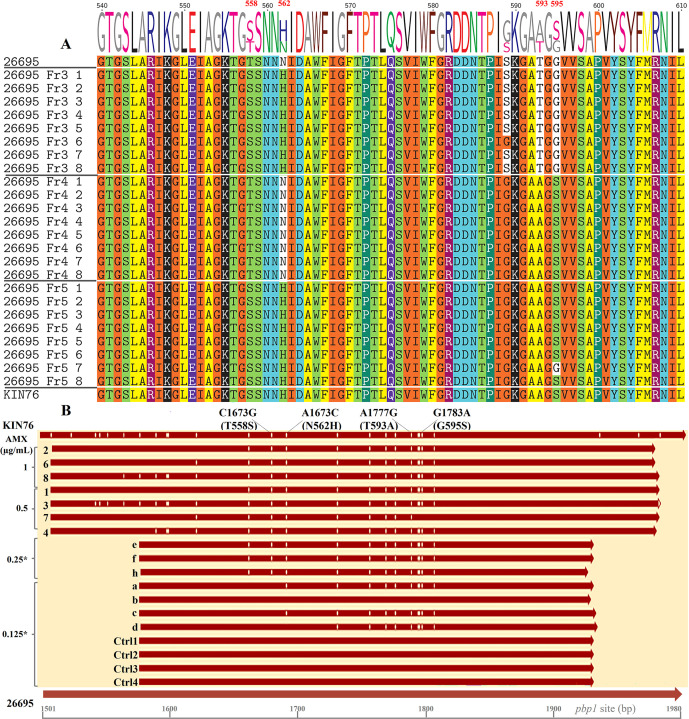
Fig 2.
Alignment of PBP1A amino acid and pbp1 nucleotide sequences. (A) Alignment of PBP1A amino acid sequences. After Sanger sequencing and initial processing of the raw data, the pbp1 gene fragments from transformants were aligned with sequences from the WT 26695 strain and the KIN76 clinical strain, then translated into protein sequences. T558 and N562 of strain 26695 were substituted by S and H in all transformant strains obtained by transformation with the Fr3 DNA fragment, except one strain (26695_Fr3-6) that contained not-AMX-R-related G589, same as strain KIN76. T593 and G595 of strain 26695 were substituted by A and S in transformant strains obtained by transformation with the Fr4 DNA fragment in all strains. Similarly, in transformants resulting from transformation with the Fr5 DNA fragment, substitutions occurred on all four loci in every strain sequenced except for one strain (26695_Fr5-7) that showed a conserved G595. (B) Nucleotide sequences of Fr5 and control strains. All the Fr5 strains (Fr5-1 to Fr5-8) were transformed using the Fr5 amplicon, and their MICs, determined later, ranged from 0.25 to 1 µg/mL. The asterisk indicates that each colony of the strain was selected on a plate containing AMX at the indicated concentration. Sequences Fr5-05 (e, f, and h) derive from strains selected on plates containing 0.5 µg/mL AMX, whereas sequences Fr5-0125 (a–d) are from Fr5-transformant strains picked from non-selective plates with 0.125 µg/mL AMX. Control sequences (Ctrl1 to Ctrl4) are from control colonies picked from non-selective plates. All sequences were aligned to the pbp1 gene of WT strains 26695 and KIN76, spanning nucleotides 1,501 to 1,980. Vertical lines within the sequences denote nucleotide variation sites in comparison to the 26695 sequence. Mutation sites are indicated at the top of the figure.