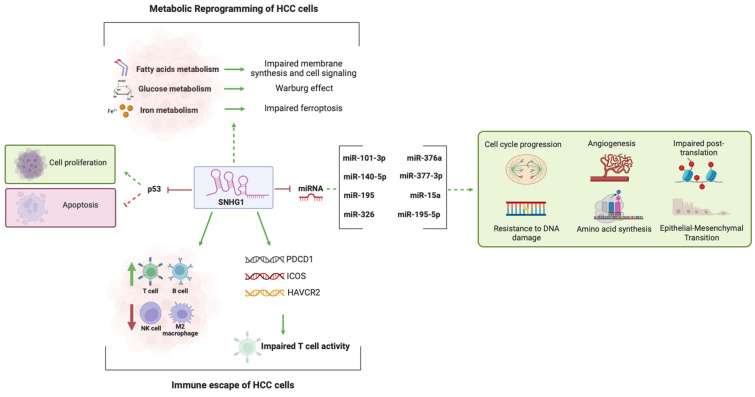
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration depicting the molecular and cellular mechanisms through which SNHG1 influences the progression of HCC. Through the inhibition of p53 and its target genes, SNHG1 stimulates cell survival and proliferation, while inhibiting proapoptotic signaling. SNHG1 also impairs the metabolism of FA, iron, and glucose, contributing to the metabolic reprogramming in HCC cells. SNHG1 interacts with a diverse network of miRNAs, inducing cellular processes crucial for carcinogenesis, like inhibition of cell cycle arrest, angiogenesis, EMT, and defective DNA repair and post-translation processes. By influencing the recruitment of specific immune cells and stimulating the expression of important genes, SNHG1 promotes the escape of HCC cells from crucial immune checkpoints. Dotted lines indicate that multiple steps have been omitted, showing only the end outcome. Green arrows indicate the promotion of a process/increase of expression/production and red arrows indicate inhibition of a process/decrease of expression/production. Created with Biorender.com.