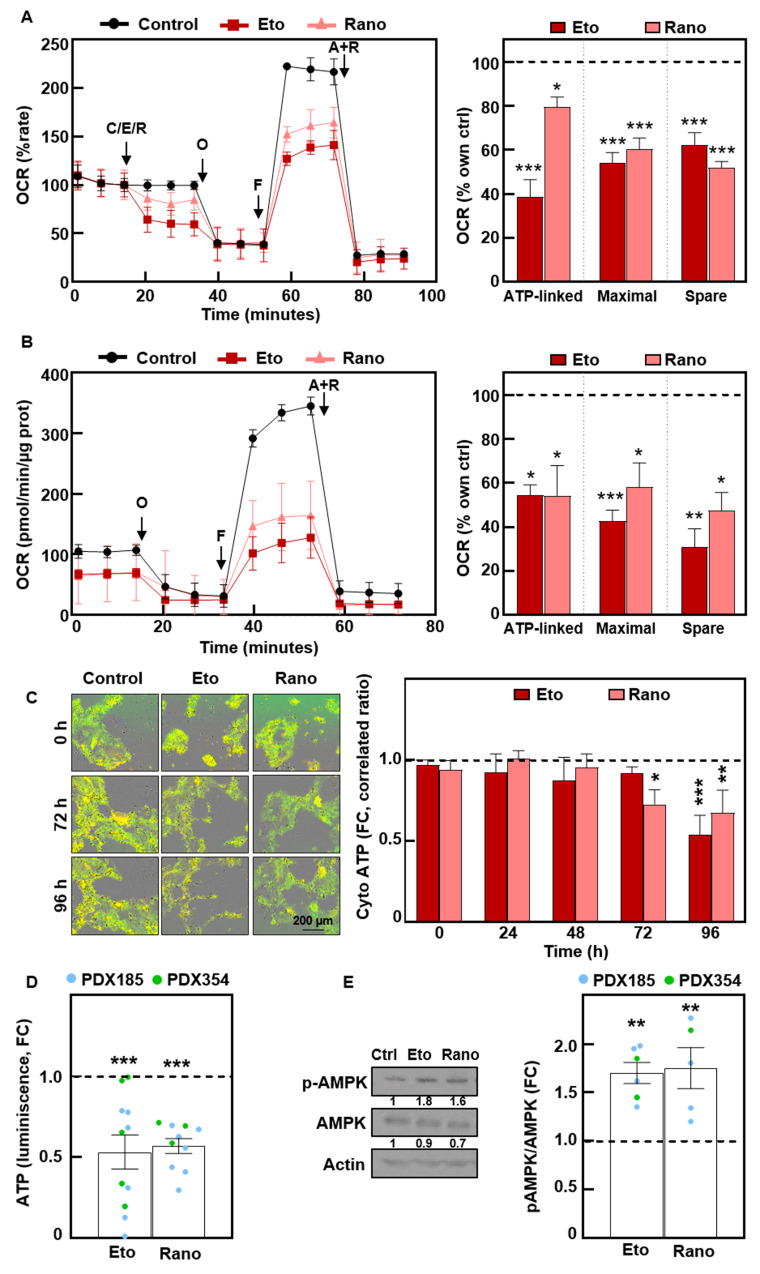
Fig. 6.
Treatment with Etomoxir and Ranolazine impairs mitochondrial respiration, inducing energy stress. (A) Long Chain FAO Stress Test with acute injections of 100 µM Etomoxir (Eto) or 50 µM Ranolazine (Rano). Left, Oxygen Consumption Rate (OCR) kinetics. Right, ATP-linked, maximal and spare respiration. Pooled data for 354 and CTCA cells. O, Oligomycin; F, FCCP; A + R, Antimycin A + Rotenone. (B) Mito Stress after 72 h of treatment of PDX215 cells with Etomoxir or Ranolazine. Left, OCR kinetics. Right, ATP-linked, maximal and spare respiration. (C) Cytosolic ATP levels in PDX215 cells visualized by time-lapse fluorescence microscopy (0–96 h). Left, representative images at the indicated times. Right, quantification. (D) Total ATP levels quantified by bioluminescence at 48 h. (E) Western blot analysis of phospho-AMPK and total AMPK after 48 h of treatment. Left, representative experiment in PDX185. Right, densitometric analysis. β-Αctin was used as loading control. The data are presented as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001