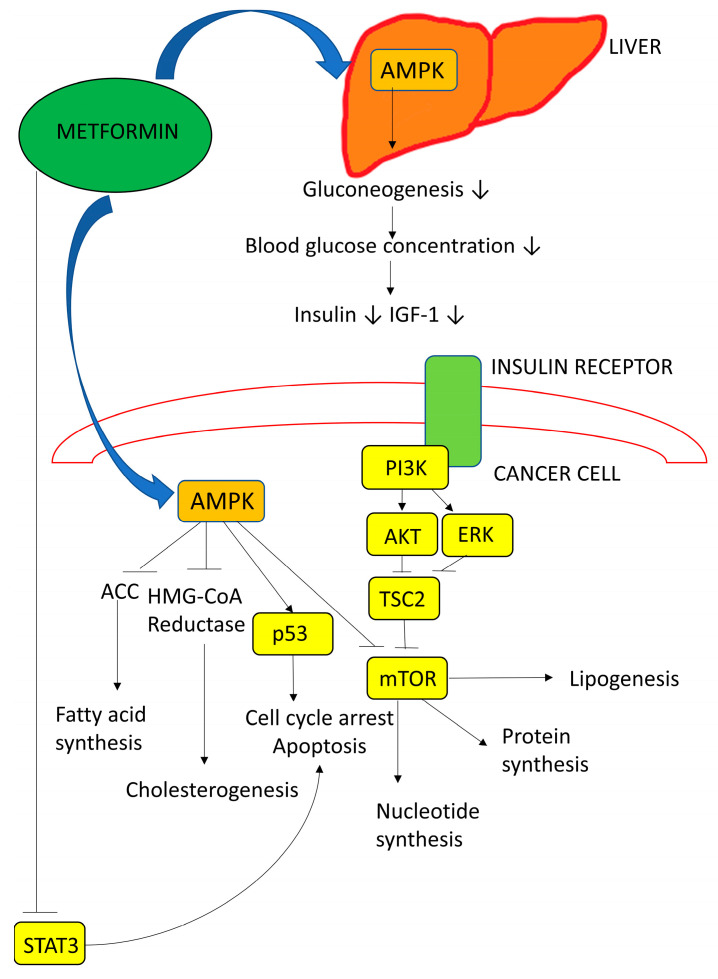
Figure 4.
Metformin has both direct and indirect effects on cancer cells. It activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), leading to the inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). It also sensitizes tissues to insulin, reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis, and decreases circulating insulin levels. This leads indirectly to reduced phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling. IGF-1 = insulin-like growth factor 1, ACC = acetyl-CoA carboxylase, HMG-CoA = 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutarylcoenzyme A, p53 = tumor protein p53, AKT = serine/threonine-specific protein kinase, and STAT3 = signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, ↓ decreasing effect, ⊥ inhibitory effect [25,26].