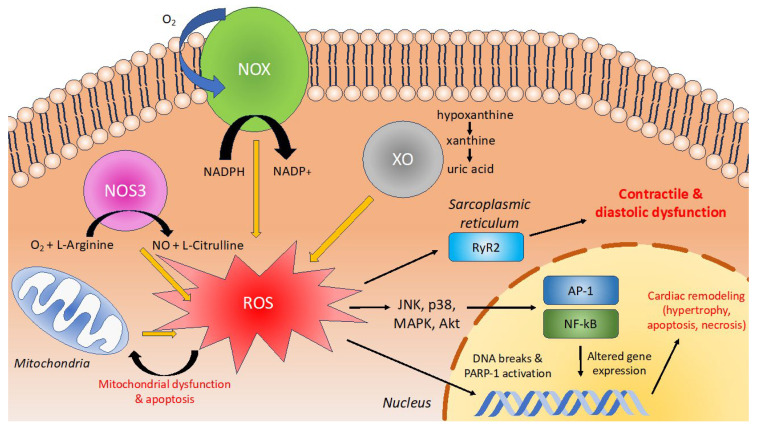
Figure 5.
ROS contribute to the pathogenesis of HF in cardiomyocytes. Under normal conditions, nitric oxide synthase (NOS3) catalyzes the conversion of O2 + L-Arginine ⇌ NO + L-Citrulline. During conditions of oxidative stress, uncoupling of NOS3 due to oxidation of BH4 leads to the production of harmful ROS. NADPH oxidase is a cytosolic enzyme responsible for the oxidation of NADPH by the equation: NADPH + 2O2 ⇌ NADP+ + 2O2− + H+. This generates two superoxide (O2−) radicals as a byproduct of the reaction. Xanthine oxidase (XO) first converts hypoxanthine to xanthine, then further oxidizes it to produce uric acid. This is performed by equations: (1) hypoxanthine + H2O + O2 ⇌ xanthine + H2O2, and (2) xanthine + H2O + O2 ⇌ uric acid + H2O2. Occasionally, mitochondria produce ROS due to the “leakage” of electrons during cellular respiration. This is mainly in the form of O2− radicals. Abbreviations: RyR2 = ryanodine receptor 2, ERK = Extracellular signal-regulated kinase. JNK = Jun nuclear kinase, MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase, and AP-1 = activator protein-1.