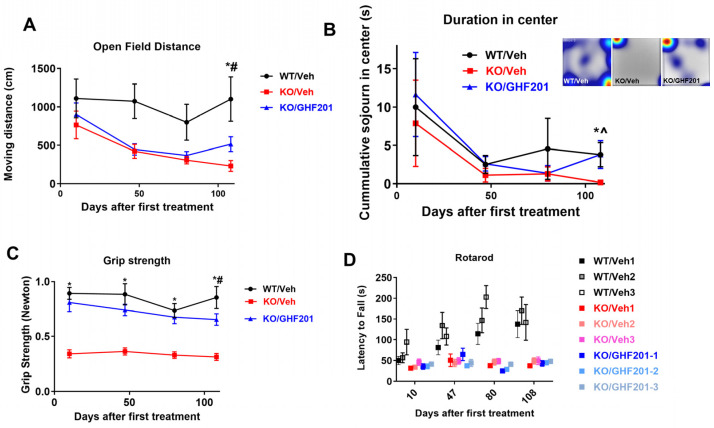
Figure 2.
Movement distance (A), sojourn in the center of an open field arena (inset representative open field sojourn heatmaps) (B), grip strength (C), and latency to fall from a rotating rod (D) were measured in n = 8 Agl−/− mice treated with 10% DMSO vehicle (KO/Veh), n = 6 wild type mice treated with vehicle (WT/Veh), and n = 10 Agl−/− mice treated with GHF-201 (KO/GHF-201). In (D), each rotarod session included three consecutive runs (1–3), separated by 10 min pauses. Two Way ANOVA with repeated measures shows that only in (C) GHF-201 treatment values were higher than vehicle-treated values in KO mice throughout the period (p < 0.05). Linear regression analysis of overall latency over time (D), shows that WT animals developed a significantly higher learning capacity than KO/Veh and KO/GHF-201 mice. Training capacity, shown by increase in latency over runs, was only demonstrated in WT mice 80 days post-treatment initiation. See text for statistical analysis. *, KO/GH201 is significantly different from KO/Veh; *#, KO/GHF-201 is significantly different from both KO/Veh and WT/Veh; *^, KO/GHF-201 is significantly different only from KO/Veh and not from WT/Veh (correction effect). Difference significance determined by multiple t-tests with Sidak post hoc correction. All error bars represent s.e.m.