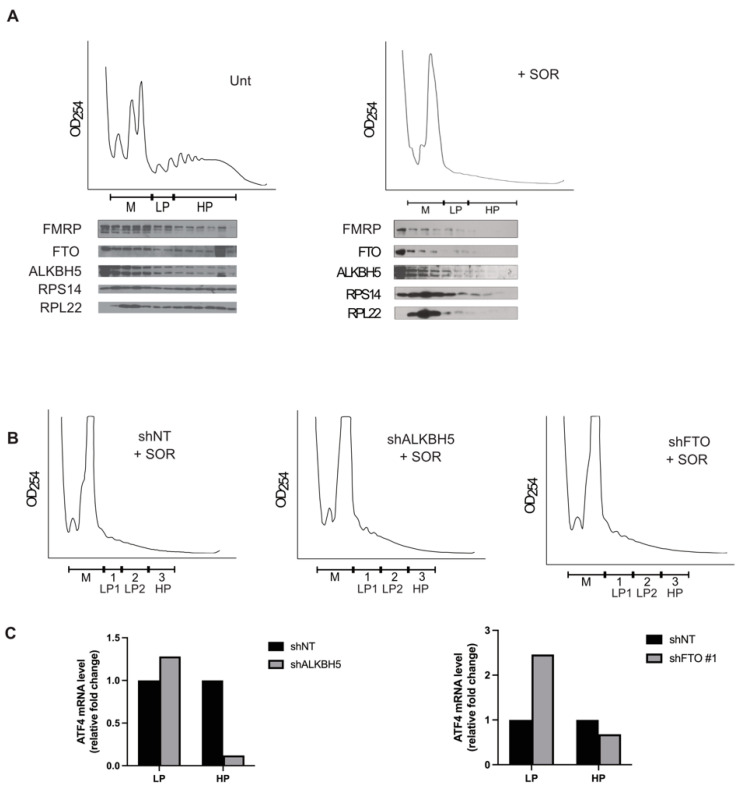
Figure 2.
Both ALKBH5 and FTO are required for the association of ATF4 mRNA with polysomes in SOR-treated Hep3B. (A) Analysis of ALKBH5 and FTO association with polysomes. Top panels: cytoplasmic extracts prepared from either untreated or SOR-treated Hep3B were fractionated through 15–55% (w/v) sucrose density gradients, and their polysome profiles were monitored by measuring the OD254. M: monosomes. LP: light polysomes. HP: heavy polysomes. Bottom panels: Western blot analysis of the collected fractions for the distribution of FMRP, ALKBH5, and FTO using specific antibodies. RPS14 and RPL22 ribosomal proteins are used as controls for the integrity of the polysome profiles. The results are representative of two independent experiments. Original images can be found in Supplementary Materials. (B,C) Analysis of the ATF4 mRNA association with polysomes in the absence of the RNA demethylases ALKBH5 and FTO. Hep3B stably expressing shRNAs against ALKBH5 or FTO or a non-specific shRNA (NT) control were treated with SOR (10 µM, two hours) as above. Cytoplasmic extracts were fractionated through 15–55% sucrose gradients, and their polysome profiles were recorded as above. (B) Polysome profile of SOR-treated Hep3B shNT, shALKBH5 and shFTO. (C) RNA content was isolated from pooled LP and HP fractions, and associated ATF4 mRNA was quantified by RT-qPCR using the ΔΔCt method. ATF4 mRNA levels were normalized against 18S ribosomal RNA and expressed as indicated. The results are representative of two independent experiments.