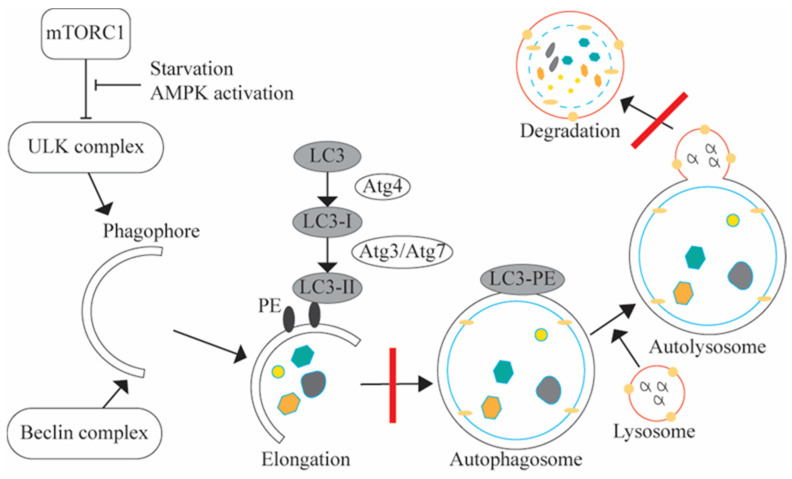
Figure 1.
Generalized Autophagy Pathway. Red slashes denote the two positions within the pathway where the multi-omics results support dysregulation within the autophagy pathway. Four of the five phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) recorded in our experiment were down in the delirium group. PE (black ovals) is critical to the elongation process in autophagy. Autophagy is a catabolic pathway that degrades cytosolic contents and is important for balancing energy stores in response to nutrient deprivation. It starts with the formation of the phagophore, which goes through an elongation process to form an autophagosome. A cytosolic microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3) (denoted in grey) is conjugated to PE to form LC3-PE. Then, the mature autophagosome fuses with the lysosome. After fusion, lysosomal proteases, like cathepsin D (CTSD), degrade the contents of the autophagosome [59]. Our proteomics results showed a decline in CTSD in the delirium group, inferring a potential build-up of autophagosomes and, ultimately, the dysregulation of the autophagy pathway.