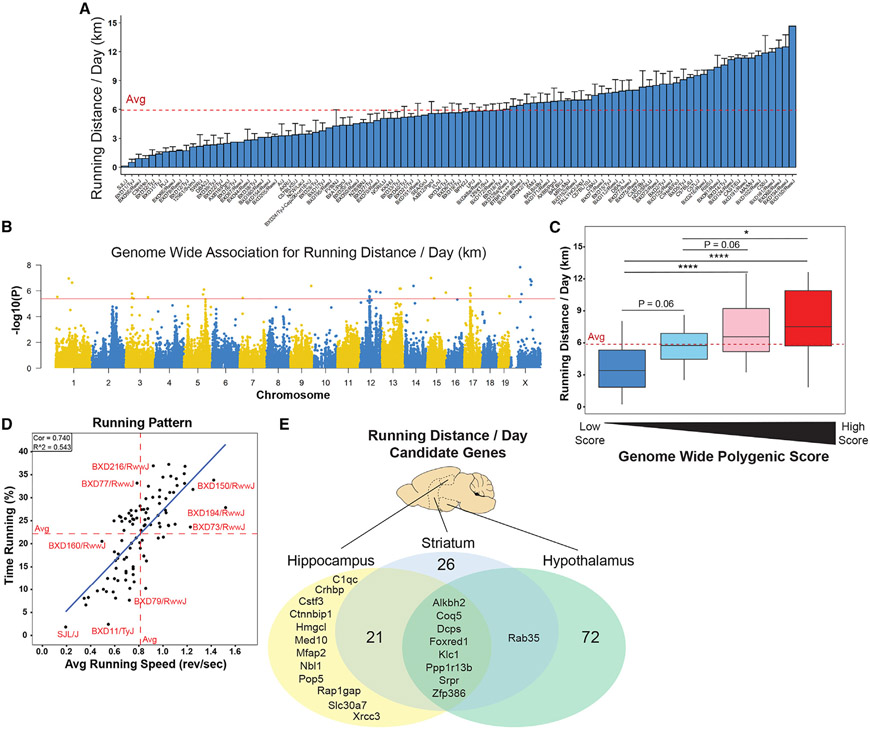
Figure 1. The impact of genetic variation and central regulators of voluntary exercise.
Female mice from the Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel (HMDP) were trained (TRN) using in-cage running wheels or remained sedentary (SED) for 30 days. Transcriptomics data from the MyoGlu study of normal-weight and overweight individuals subjected to both acute and long-term endurance exercise were integrated for subsequent comparative analyses and made publicly available in a Shiny Web application.
(A) Average daily running distance (km), dashed line indicates average.
(B) GWAS for average daily running distance, solid line indicates significance threshold.
(C) Genome-wide polygenic score for running distance per day (km) of strains stratified by quartile; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Only using SNPs with between r2 < 0.6 and GWAS p < 0.01. Dashed line indicates overall average.
(D) Correlation of average running speed (revolutions/s) with percentage time running (% of 24-h period); solid blue line indicates least-squares regression line. Dashed lines indicate axis strain average.
(E) Venn diagram showing overlap of candidate gene analysis for average daily running vs. previously published HMDP of RNA sequencing in hippocampus, hypothalamus, and striatum. Correlations were considered significant at FDR < 0.05.