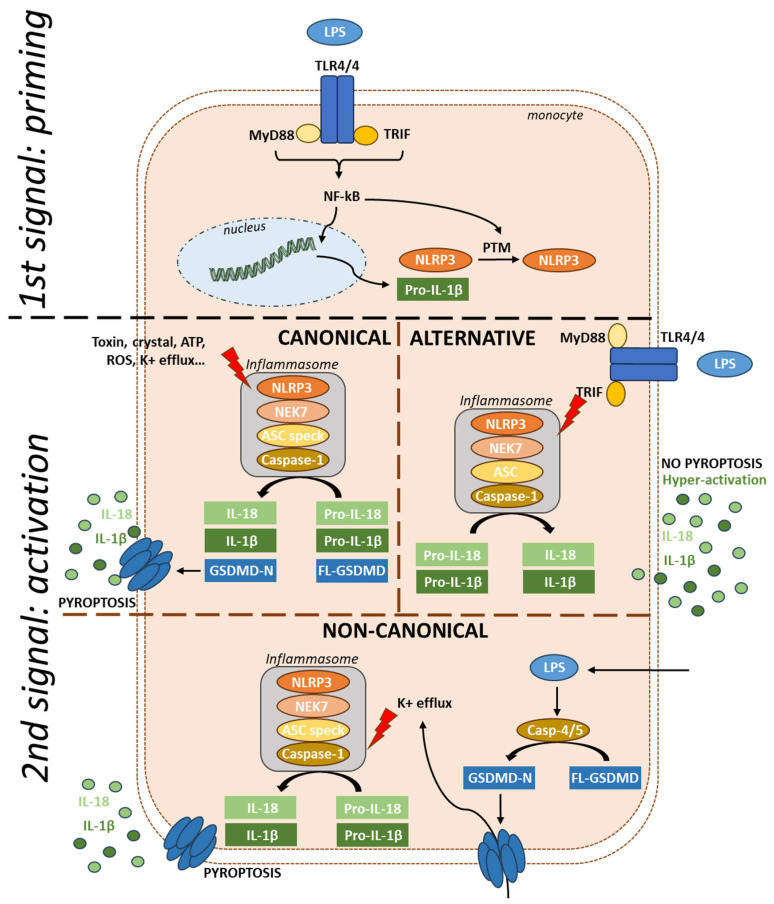
Figure 2.
Activation mechanisms of NLRP3. The priming signal induces the production of NLRP3 and pro-IL-1β via TLR-NF-kB signaling, followed by a series of post-translational modifications. In canonical activation, the second signal, triggered by various activators, leads to the formation of the inflammasome with NEK7, ASC, and caspase-1. Once activated, the inflammasome cleaves pro-cytokines into their active forms and also cleaves gasdermin, leading to pyroptosis. In the alternative pathway, LPS via TLR4 signaling leads to the production of NLRP3 and pro-IL-1β. Dual activation through TRIF then activates the inflammasome, resulting in hyperactivation without pyroptosis and no ASC speck formation. In the non-canonical pathway, intracellular LPS serves as the second signal, activating caspases 4 and 5, which cleave gasdermin, leading to pyroptosis. Pores in the membrane cause K+ efflux, triggering NLRP3 inflammasome formation. FL-GSDMD: Full-length gasdermin; GSDMD-N: Gasdermin-N-terminal; NF-kB: Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.