Abstract
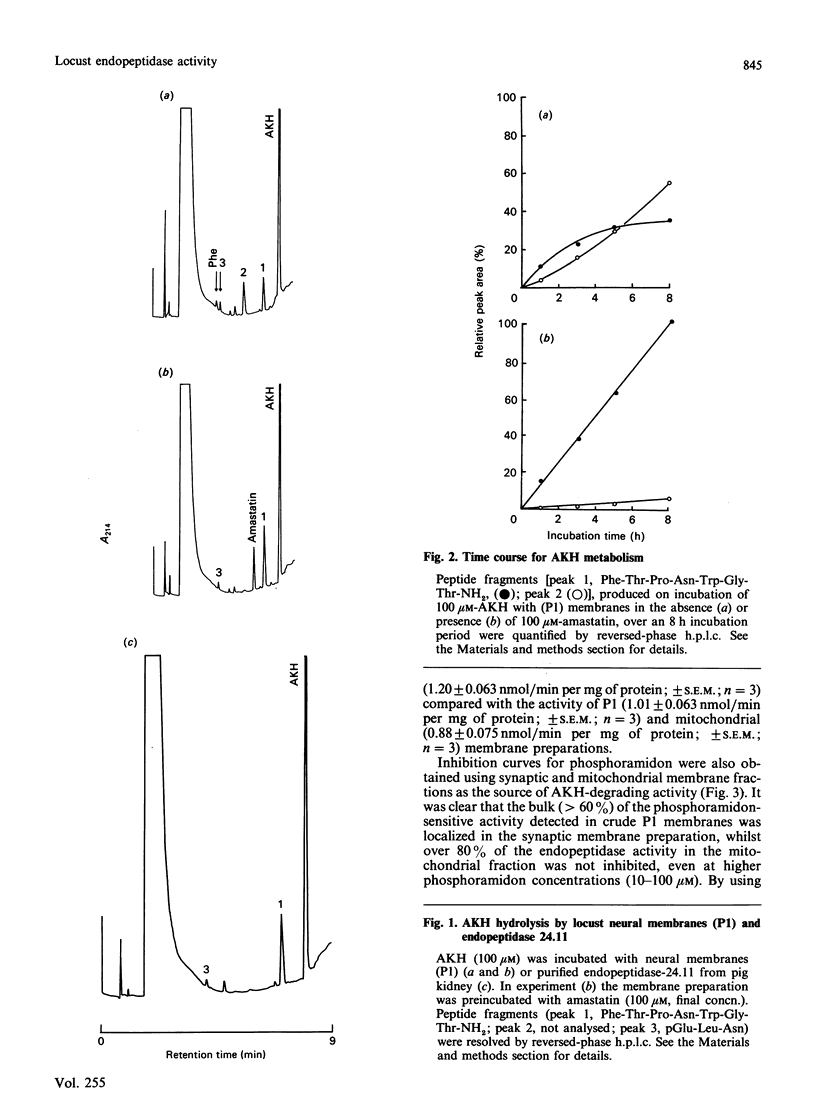
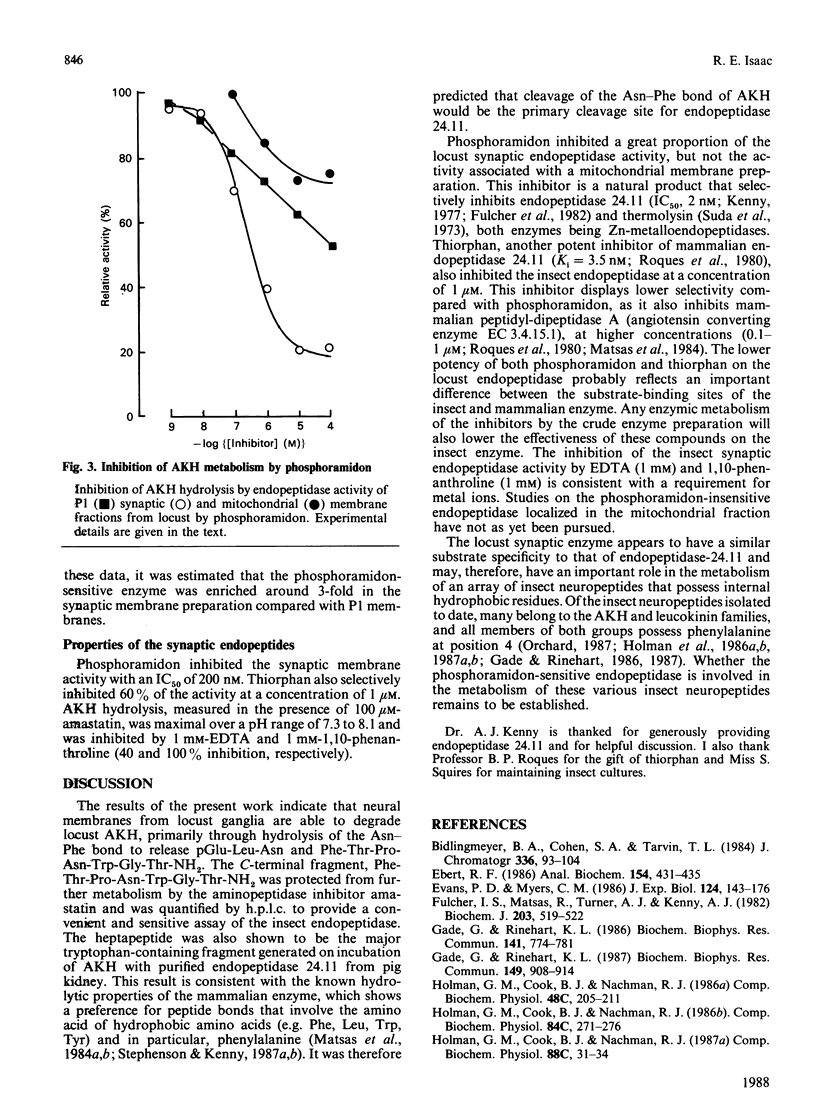
Locust adipokinetic hormone (AKH, pGlu-Leu-Asn-Phe-Thr-Pro-Asn-Trp-Gly-Thr-NH2) was used as the substrate to measure neuropeptide-degrading endopeptidase activity in neutral membranes from ganglia of the locust Schistocerca gregaria. Initial hydrolysis of AKH at neural pH by peptidases of washed neural membranes generated pGlu-Leu-Asn and Phe-Thr-Pro-Asn-Trp-Gly-Thr-NH2 as primary metabolites, demonstrating that degradation was initiated by cleavage of the Asn-Phe bond. Amastatin protected the C-terminal fragment from further metabolism by aminopeptidase activity without inhibiting AKH degradation. The same fragments were generated on incubation of AKH with purified pig kidney endopeptidase 24.11, and enzyme known to cleave peptide bonds that involve the amino group of hydrophobic amino acids. Phosphoramidon (10 microM), a selective inhibitor of mammalian endopeptidase 24.11, partially inhibited the endopeptidase activity of locust neural membranes. This phosphoramidon-sensitive activity was shown to enriched in a synaptic membrane preparation with around 80% of the activity being inhibited by 10 microM-phosphoramidon (IC50 = 0.2 microM). The synaptic endopeptidase was also inhibited by 1 mM-EDTA, 1 mM-1,10-phenanthroline and 1 microM-thiorphan, and the activity was maximal between pH 7.3 and 8.0. Localization of the phosphoramidon-sensitive enzyme in synaptic membranes is consistent with a physiological role for this endopeptidase in the metabolism of insect peptides at the synapse.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert R. F. Amino acid analysis by HPLC: optimized conditions for chromatography of phenylthiocarbamyl derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):431–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Kidney neutral endopeptidase and the hydrolysis of enkephalin by synaptic membranes show similar sensitivity to inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 May 1;203(2):519–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2030519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Rinehart K. L., Jr Amino acid sequence of a hypertrehalosaemic neuropeptide from the corpus cardiacum of the cockroach, Nauphoeta cinerea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):774–781. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Rinehart K. L. Primary sequence analysis by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry of a peptide with adipokinetic activity from the corpora cardiaca of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):908–914. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac R. E. Proctolin degradation by membrane peptidases from nervous tissues of the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria). Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):365–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2450365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T. Brain peptides: what, where, and why? Science. 1983 Dec 2;222(4627):975–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6139875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKelvy J. F., Blumberg S. Inactivation and metabolism of neuropeptides. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:415–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. J., Holman G. M., Cook B. J., Haddon W. F., Ling N. Leucosulfakinin-II, a blocked sulfated insect neuropeptide with homology to cholecystokinin and gastrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. J., Holman G. M., Haddon W. F., Ling N. Leucosulfakinin, a sulfated insect neuropeptide with homology to gastrin and cholecystokinin. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.3749893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea M., Witten J., Schaffer M. Isolation and characterization of two myoactive neuropeptides: further evidence of an invertebrate peptide family. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):521–529. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00521.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Jamieson G. C., Kalish F., Kramer S. J., McEnroe G. A., Miller C. A., Schooley D. A. Isolation and primary structure of two peptides with cardioacceleratory and hyperglycemic activity from the corpora cardiaca of Periplaneta americana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5575–5579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooneveld H., Romberg-Privee H. M., Veenstra J. A. Adipokinetic hormone-immunoreactive peptide in the endocrine and central nervous system of several insect species: a comparative immunocytochemical approach. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1985 Feb;57(2):184–194. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(85)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooneveld H., Tesser G. I., Veenstra J. A., Romberg-Privee H. M. Adipokinetic hormone and AKH-like peptide demonstrated in the corpora cardiaca and nervous system of Locusta migratoria by immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;230(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00216028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Malfroy B., De La Baume S. Biological inactivation of enkephalins and the role of enkephalin-dipeptidyl-carboxypeptidase ("enkephalinase") as neuropeptidase. Life Sci. 1981 Oct 26;29(17):1715–1740. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. Metabolism of neuropeptides. Hydrolysis of the angiotensins, bradykinin, substance P and oxytocin by pig kidney microvillar membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj2410237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. The hydrolysis of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide by pig kidney microvillar membranes is initiated by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):183–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2430183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. V., Mordue W., Batley K. E., Morris H. R. Structure of locust adipokinetic hormone, a neurohormone that regulates lipid utilisation during flight. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):207–211. doi: 10.1038/263207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda H., Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Letter: A thermolysin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes: phospholamidon. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Oct;26(10):621–623. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Matsas R., Kenny A. J. Are there neuropeptide-specific peptidases? Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 May 1;34(9):1347–1356. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90669-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witten J. L., Schaffer M. H., O'Shea M., Cook J. C., Hemling M. E., Rinehart K. L., Jr Structures of two cockroach neuropeptides assigned by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):350–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91560-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


