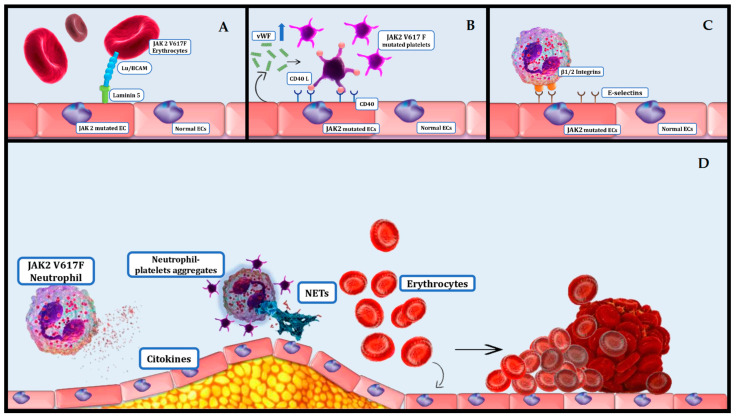
Figure 1.
Cardiovascular complications associated with MPNs. (A) Lu/BCAM (Lutheran /Basal Cell Adhesion Molecule)-mediated red cell adhesion independently of the erythropoietin receptor (EpoR), utilizing the Rap1/Akt pathway in patients with JAK2 V617F mutation increases thrombotic risk; (B) JAK2 V617F mutated endothelial cells (ECs) secrete higher amounts of von Willebrand Factor (vWF), which enhance CD 40 expression on ECs and CD40L on JAK2 V617F platelets increasing platelets adhesion; (C) JAK2 V617F mutated granulocytes express abnormal levels of β1/2 integrins that interact with selectins on ECs increasing thrombotic risk; (D) JAK2 V617F mutated granulocytes secrete high amounts of cytokines (TNF-α, IL1-β, IL-6 and G-CSF), and there is a high activity of NLPR3 and absent melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome; neutrophil–platelets aggregates are highly adherent to ECs; neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are a mixture of DNA, protein, and enzymes that facilitate thrombosis in MPNs.