Abstract
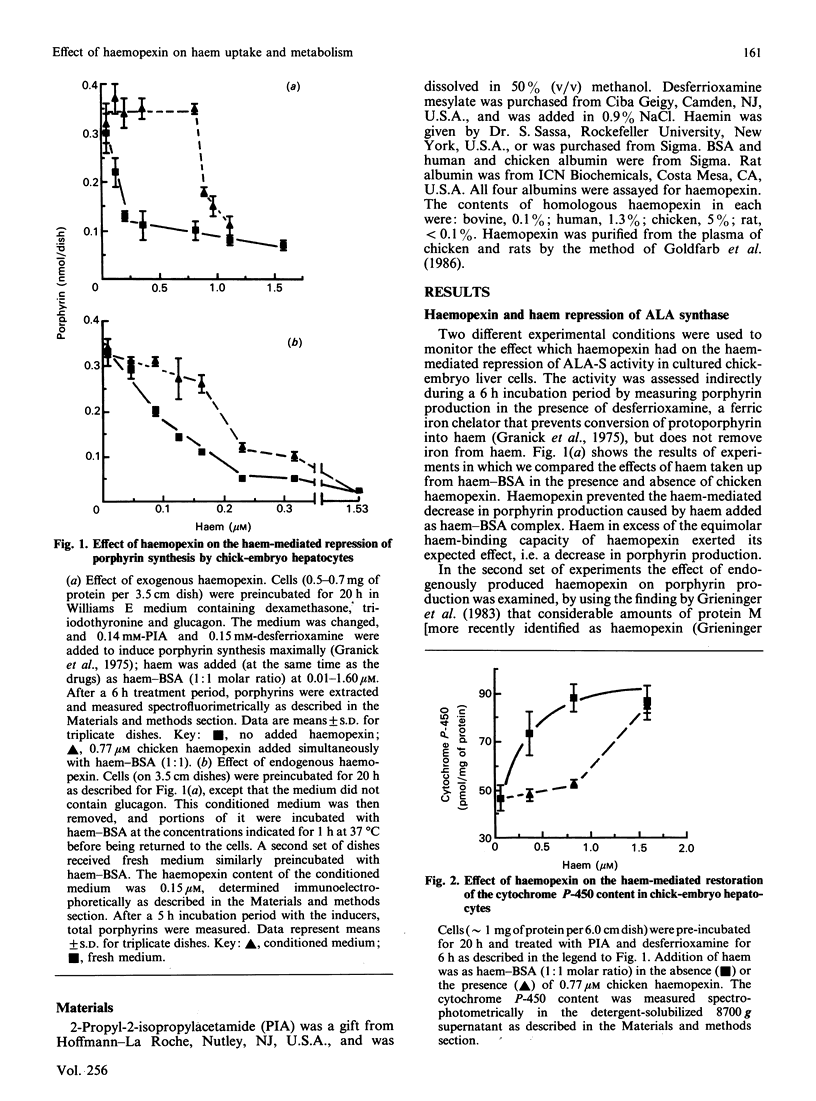
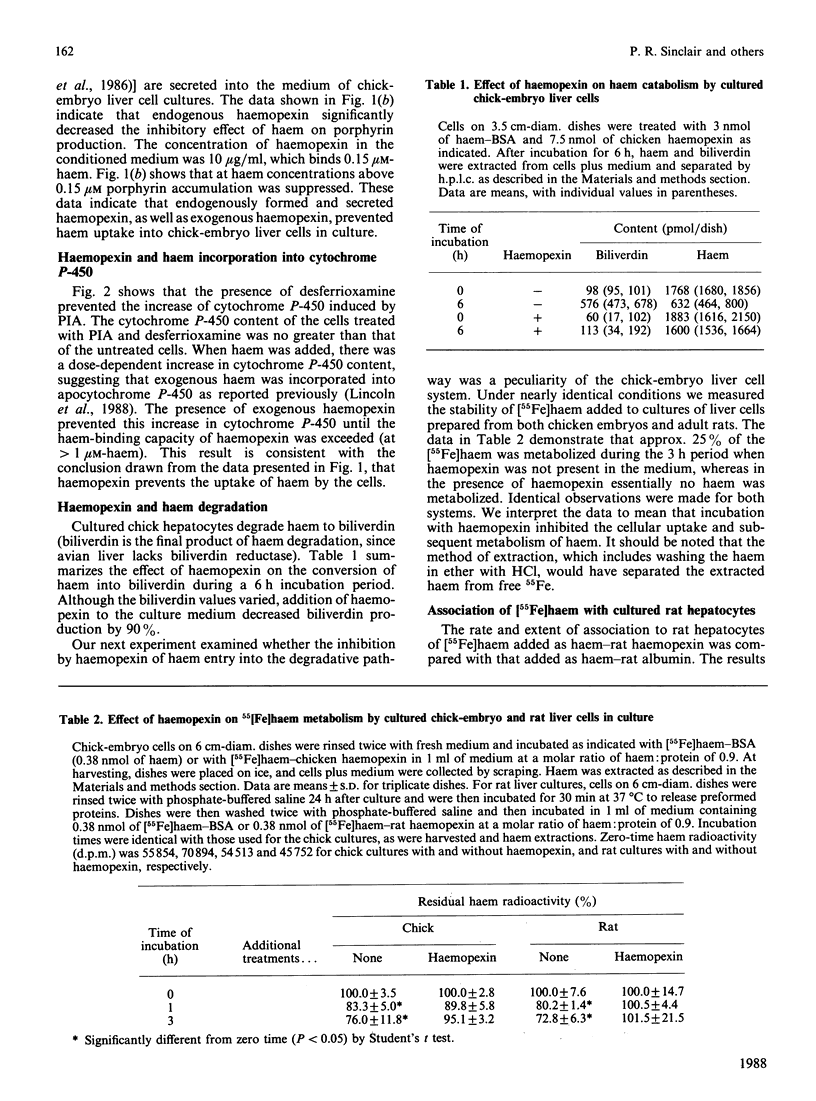
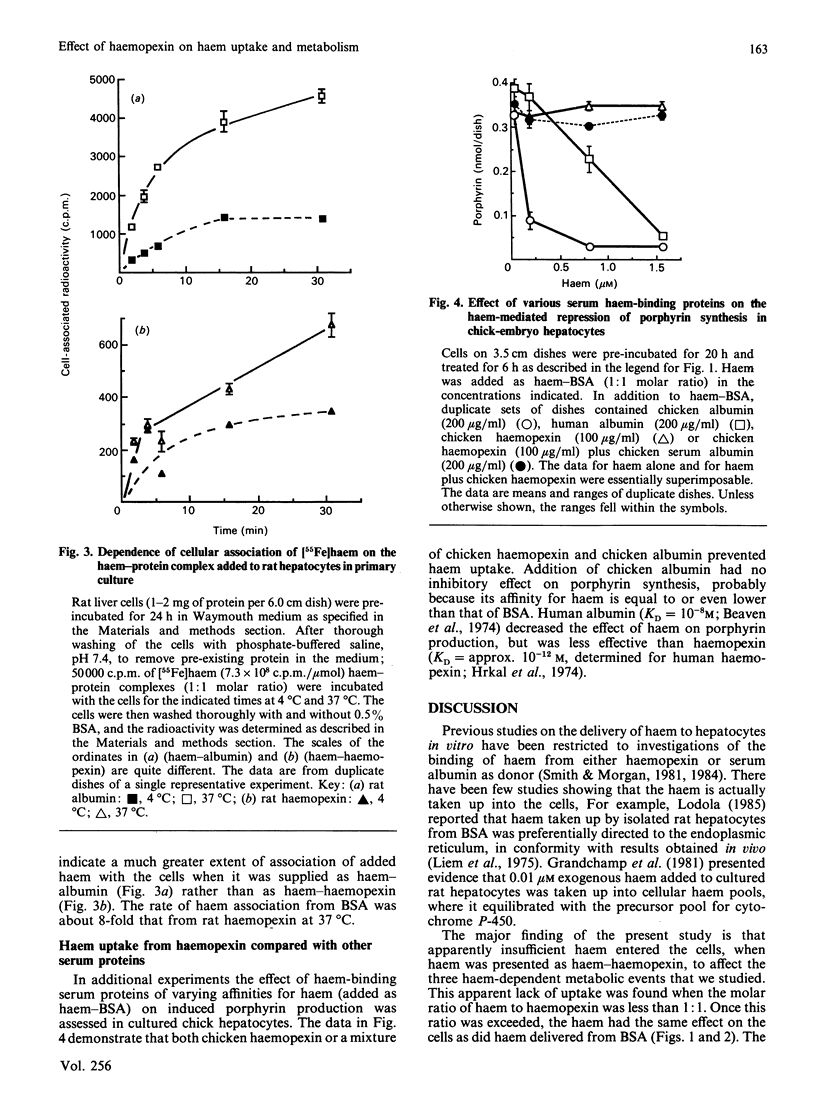
A role of haemopexin in transporting haem to hepatocytes for degradation has been inferred from the high affinity of haemopexin for haem. We have examined this question in primary cultures of chick-embryo and adult rat liver cells. We present here the results of four sets of experiments which indicate that haemopexin retarded haem uptake by hepatocytes in culture. (1) Haem bound to bovine serum albumin is known to repress the activity of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase in chick cultures as indicated by decreased porphyrin accumulation. When haem-albumin was added in the presence of excess purified or freshly secreted chicken haemopexin, no haem-mediated repression of porphyrin production was observed. The haem-mediated repression of porphyrin accumulation was partially prevented when human, but not chicken, albumin was added to cultures. This finding reflected the higher affinity of human albumin for haem compared with that of chicken albumin. (2) Haemopexin inhibited the ability of haem to be incorporated into cytochrome P-450 induced in the chick cultures in the presence of the iron chelator desferrioxamine. (3) The rate of association of [55Fe]haem with cultured rat hepatocytes when [55Fe]haem-haemopexin was added was one-eighth of the rate observed when [55Fe]haem-bovine serum albumin was used as the haem donor. (4) The presence of haemopexin also diminished the catabolism of haem by both rat and chick-embryo liver cell cultures. It is concluded that the uptake and subsequent metabolic effects of haem are inhibited in cultured hepatocytes by proteins such as haemopexin which have a high affinity for haem.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ades I. Z., Stevens T. M., Drew P. D. Biogenesis of embryonic chick liver delta-aminolevulinate synthase: regulation of the level of mRNA by hemin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Mar;253(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven G. H., Chen S. H., d' Albis A., Gratzer W. B. A spectroscopic study of the haemin--human-serum-albumin system. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 1;41(3):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell D. M., Liem H. H., Muller-Eberhard U. Secretion of haem by hepatic parenchymal cells. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 15;184(3):689–694. doi: 10.1042/bj1840689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonkovsky H. L., Wood S. G., Howell S. K., Sinclair P. R., Lincoln B., Healey J. F., Sinclair J. F. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation and quantitation of tetrapyrroles from biological materials. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):56–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornheim L. M., Underwood M. C., Caldera P., Rettie A. E., Trager W. F., Wrighton S. A., Correia M. A. Inactivation of multiple hepatic cytochrome P-450 isozymes in rats by allylisopropylacetamide: mechanistic implications. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;32(1):299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. M., Smith A., Muller-Eberhard U., Morgan W. T. Hepatic subcellular metabolism of heme from heme-hemopexin: incorporation of iron into ferritin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 28;91(4):1504–1511. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer P. W., Stephens J. K., Marks G. S. Effect of varying the insulin to glucagon ratio on porphyrin biosynthesis in chick embryo liver cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;14(4):717–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith R. A., Sassa S., Kappas A. Heme binding to murine erythroleukemia cells. Evidence for a heme receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12198–12202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb V., Trimble R. B., De Falco M., Liem H. H., Metcalfe S. A., Wellner D., Muller-Eberhard U. An avian serum alpha 1-glycoprotein, hemopexin, differing significantly in both amino acid and carbohydrate composition from mammalian (beta-glycoprotein) counterparts. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6555–6562. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandchamp B., Bissell D. M., Licko V., Schmid R. Formation and disposition of newly synthesized heme in adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11677–11683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granick S., Sinclair P., Sassa S., Grieninger G. Effects by heme, insulin, and serum albumin on heme and protein synthesis in chick embryo liver cells cultured in a chemically defined medium, and a spectrofluorometric assay for porphyrin composition. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9215–9225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieninger G., Liang T. J., Beuving G., Goldfarb V., Metcalfe S. A., Muller-Eberhard U. Hemopexin is a developmentally regulated, acute-phase plasma protein in the chicken. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15719–15724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieninger G., Plant P. W., Liang T. J., Kalb R. G., Amrani D., Mosesson M. W., Hertzberg K. M., Pindyck J. Hormonal regulation of fibrinogen synthesis in cultured hepatocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:469–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healey J. F., Bonkowsky H. L., Sinclair P. R., Sinclair J. F. Conversion of 5-aminolaevulinate into haem by liver homogenates. Comparison of rat and chick embryo. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):595–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1980595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrkal Z., Vodrázka Z., Kalousek I. Transfer of heme from ferrihemoglobin and ferrihemoglobin isolated chains to hemopexin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 15;43(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem H. H., Tavassoli M., Muller-Eberhard U. Cellular and subcellular localization of heme and hemopexin in the rabbit. Acta Haematol. 1975;53(4):219–225. doi: 10.1159/000208186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln B. C., Healey J. F., Bonkovsky H. L. Regulation of hepatic haem metabolism. Disparate mechanisms of induction of haem oxygenase by drugs and metals. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):189–196. doi: 10.1042/bj2500189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodola A. A characterization of haem uptake and intracellular distribution by isolated hepatocytes. Biosci Rep. 1985 Jul;5(7):609–614. doi: 10.1007/BF01117074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majuri R., Gräsbeck R. A rosette receptor assay with haem-microbeads. Demonstration of a haem receptor on K562 cells. Eur J Haematol. 1987 Jan;38(1):21–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1987.tb01418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T. Porphyrin-binding proteins in serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:624–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard U., Bosman C., Liem H. H. Tissue localization of the heme-hemopexin complex in the rabbit and the rat as studied by light microscopy with the use of radioisotopes. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Sep;76(3):426–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard U., Javid J., Liem H. H., Hanstein A., Hanna M. Plasma concentrations of hemopexin, haptoglobin and heme in patients with various hemolytic diseases. Blood. 1968 Nov;32(5):811–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard U., Vincent S. H. Concepts of heme distribution within hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 15;34(6):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90749-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHINOWARA G. Y., WALTERS M. I. HEMATIN--STUDIES ON PROTEIN COMPLEXES AND DETERMINATION IN HUMAN PLASMA. Am J Clin Pathol. 1963 Aug;40:113–122. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/40.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedlofsky S. I., Sinclair P. R., Bonkovsky H. L., Healey J. F., Swim A. T., Robinson J. M. Haem synthesis from exogenous 5-aminolaevulinate in cultured chick-embryo hepatocytes. Effects of inducers of cytochromes P-450. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):229–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2480229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. F., Sinclair P. R., Bonkowsky H. L. Hormonal requirements for the induction of cytochrome P-450 in hepatocytes cultured in a serum-free medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 14;86(3):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91771-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. F., Sinclair P. R., Healey J. F., Smith E. L., Bonkowsky H. L. Decrease in hepatic cytochrome P-450 by cobalt. Evidence for a role of cobalt protoporphyrin. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):103–109. doi: 10.1042/bj2040103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair P. R., Bement W. J., Bonkovsky H. L., Sinclair J. F. Inhibition of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase by halogenated biphenyls in chick hepatocyte cultures. Essential role for induction of cytochrome P-448. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):737–748. doi: 10.1042/bj2220737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair P. R., Granick S. The transport of hemin and protoporphyrin across the plasma membrane of chick embryo liver cells in culture. Ann Clin Res. 1976;8 (Suppl 17):250–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. Intracellular distribution of haem after uptake by different receptors. Haem-haemopexin and haem-asialo-haemopexin. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):663–669. doi: 10.1042/bj2310663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A., Morgan W. T. Haem transport to the liver by haemopexin. Receptor-mediated uptake with recycling of the protein. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):47–54. doi: 10.1042/bj1820047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A., Morgan W. T. Hemopexin-mediated heme uptake by liver. Characterization of the interaction of heme-hemopexin with isolated rabbit liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12049–12053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A., Morgan W. T. Hemopexin-mediated transport of heme into isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10902–10909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A., Morgan W. T. Transport of heme by hemopexin to the liver: evidence for receptor-mediated uptake. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 14;84(1):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W., Samuelson A. C., Johansen K. L., Nakata R., Withers D. M., Sosiak A. Influence of Cl- on organic anion transport in short-term cultured rat hepatocytes and isolated perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1259–1268. doi: 10.1172/JCI112946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


