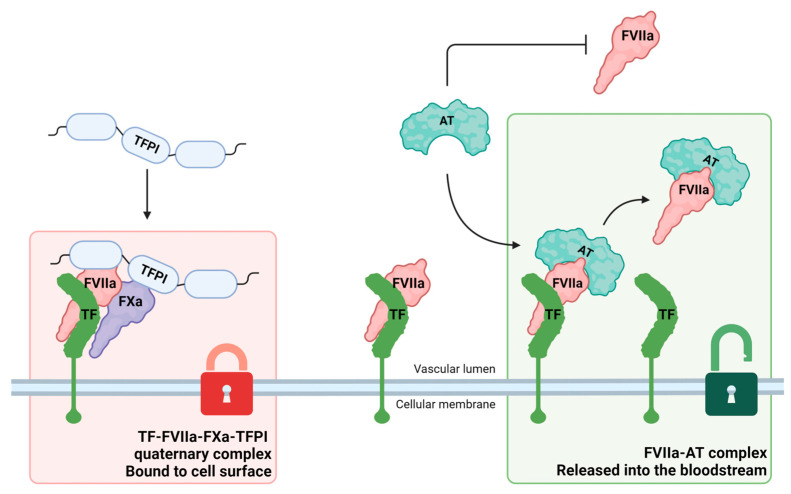
Figure 2.
Modes of action of the main inhibitors of the tissue factor (TF) pathway. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) forms a tetramolecular complex (TF–FVIIa–FXa–TFPI) which remains stable on the surface of the cell membrane (on the left). Antithrombin (AT) reacts with FVIIa only if FVIIa is bound to functionally active TF, thereby forming a FVIIa–AT complex, which is released from the cell membrane into the bloodstream (on the right). Created with BioRender.com. AT, antithrombin; FVIIa, activated factor VII; FXa, activated factor X; FVIIa–AT, activated factor VII-antithrombin; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor.