Figure 1.
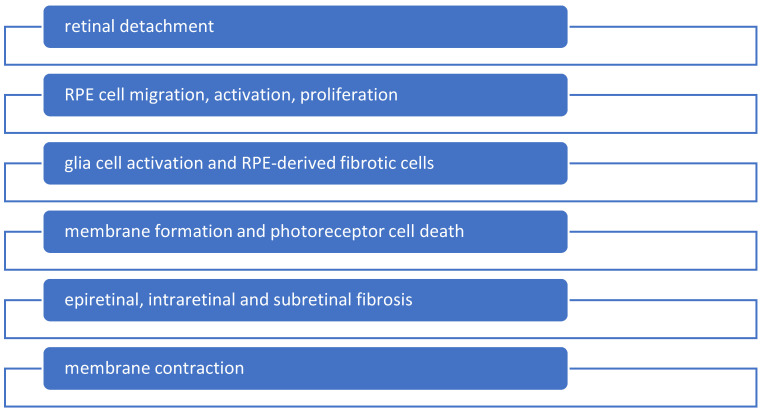
Due to retinal detachment, some molecular alterations take place in the microenvironment of the detached retina, such as the breakdown of the blood–retinal barrier, retinal hypoxia, the activation of glial and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells, and subsequent inflammation. A range of chemokines and cytokines provoke RPE activation, which results in RPE-derived fibrotic cells that give birth to membrane formation.