Abstract
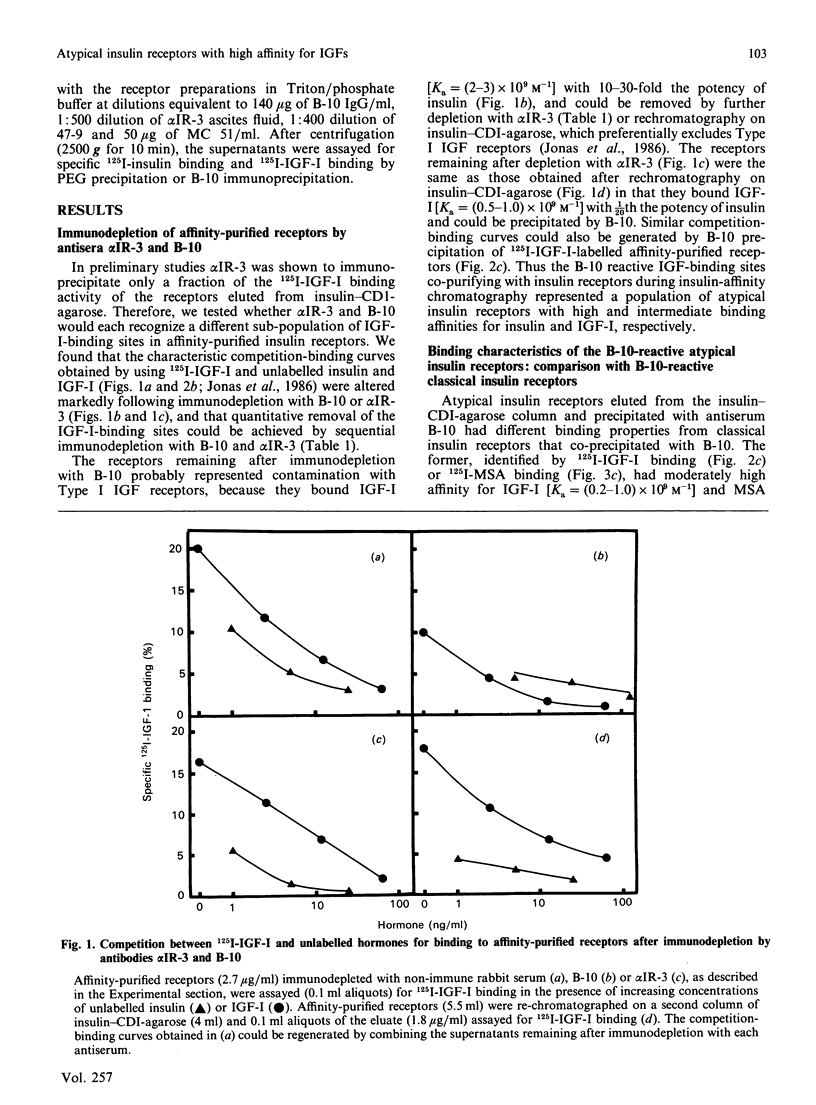
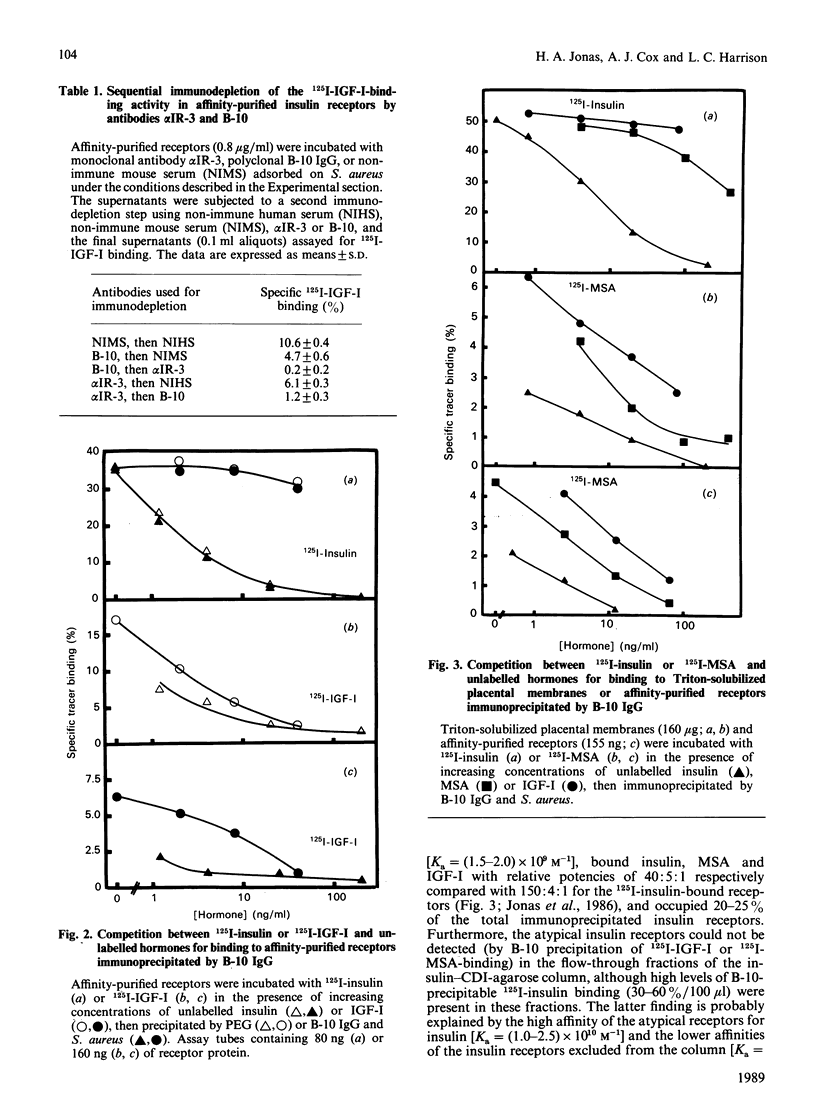
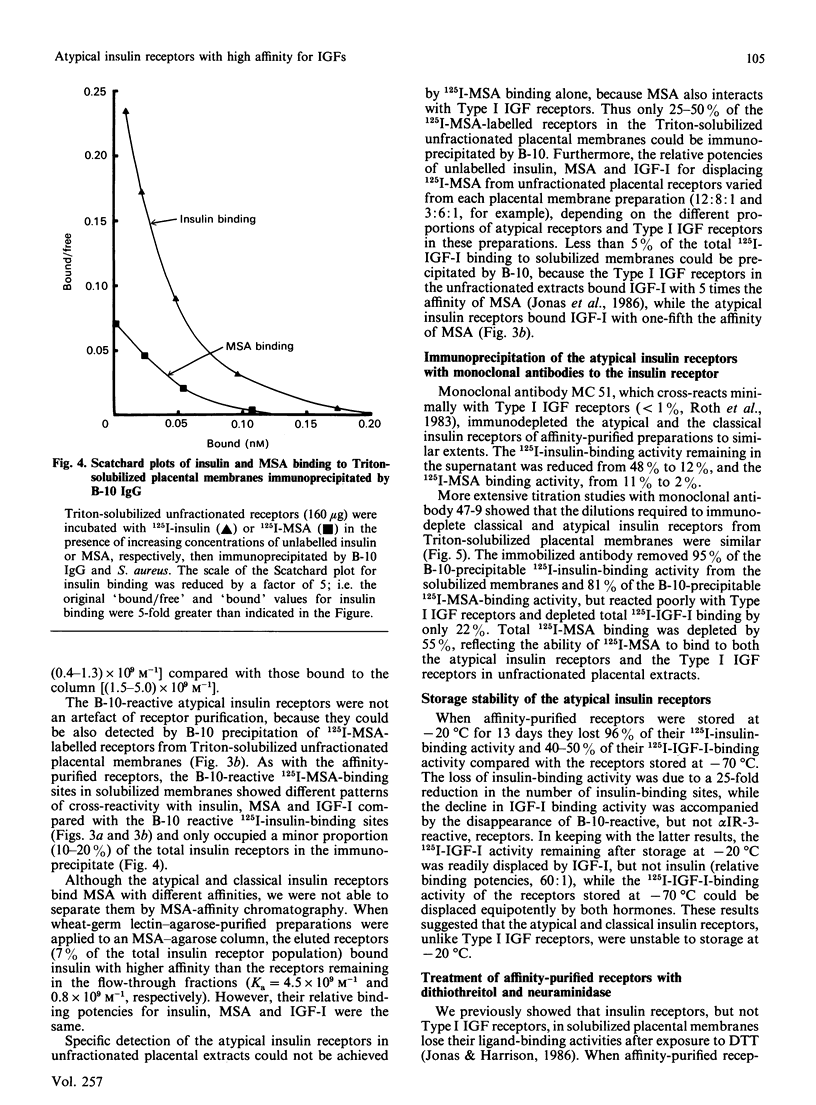
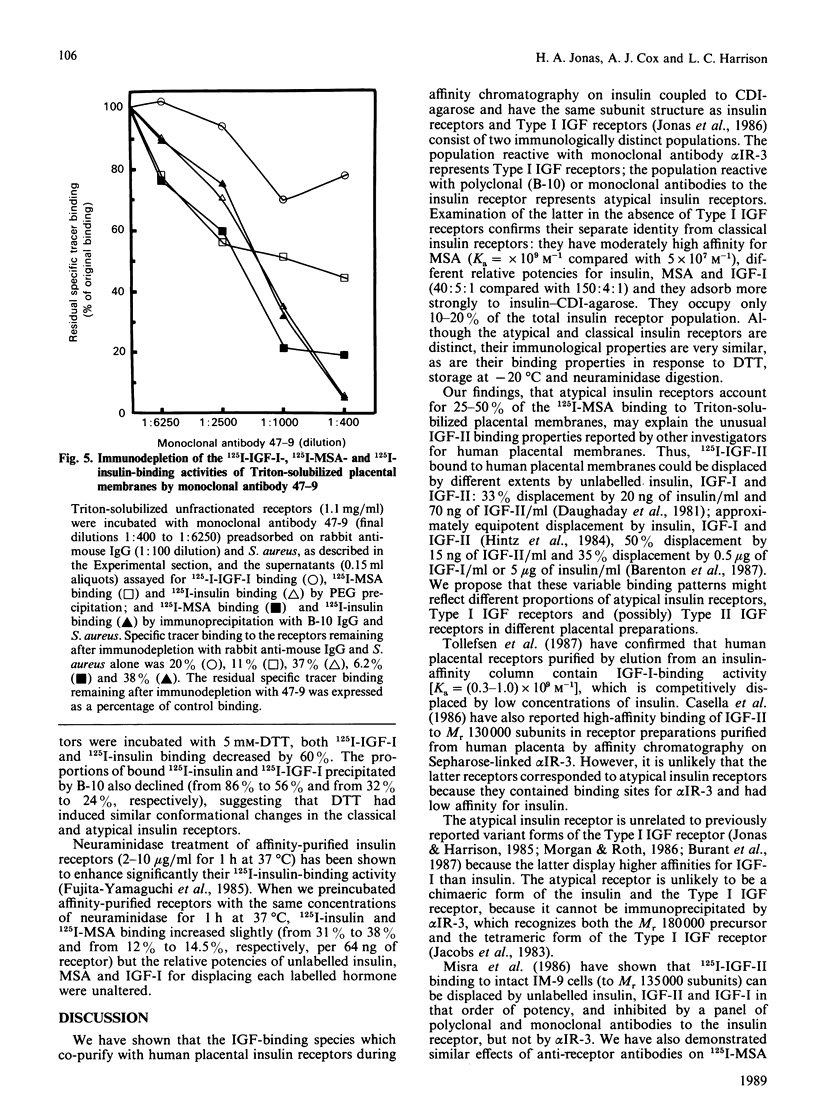
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding sites copurifying with human placental insulin receptors during insulin-affinity chromatography consist of two immunologically distinct populations. One reacts with monoclonal antibody alpha IR-3, but not with antibodies to the insulin receptor, and represents Type I IGF receptors; the other reacts only with antibodies to the insulin receptor and is precipitated with a polyclonal receptor antibody (B-10) after labelling with 125I-multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA, rat IGF-II). The latter is a unique sub-population of atypical insulin receptors which differ from classical insulin receptors by their unusually high affinity for MSA (Ka = 2 x 10(9) M-1 compared with 5 x 10(7) M-1) and relative potencies for insulin, MSA and IGF-I (40:5:1 compared with 150:4:1). They represent 10-20% of the total insulin receptor population and account for 25-50% of the 125I-MSA binding activity in Triton-solubilized placental membranes. Although atypical and classical insulin receptors are distinct, their immunological properties are very similar, as are their binding properties in response to dithiothreitol, storage at -20 degrees C and neuraminidase digestion. We conclude that atypical insulin receptors with moderately high affinity for IGFs co-exist with classical insulin receptors and Type I IGF receptors in human placenta. They provide an explanation for the unusual IGF-II binding properties of human placental membranes and may have a specific role in placental growth and/or function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Brown A. S. Purification of tracer for somatomedin C radioimmunoassay by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):485–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burant C. F., Treutelaar M. K., Allen K. D., Sens D. A., Buse M. G. Comparison of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors from rat skeletal muscle and L-6 myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella S. J., Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Insulin-like growth factor II binding to the type I somatomedin receptor. Evidence for two high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9268–9273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Mariz I. K., Trivedi B. A preferential binding site for insulin-like growth factor II in human and rat placental membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Aug;53(2):282–288. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-2-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fant M., Munro H., Moses A. C. An autocrine/paracrine role for insulin-like growth factors in the regulation of human placental growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Aug;63(2):499–505. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-2-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Sato Y., Kathuria S. Removal of sialic acids from the purified insulin receptor results in enhanced insulin-binding and kinase activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91954-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Billington T., East I. J., Nichols R. J., Clark S. The effect of solubilization on the properties of the insulin receptor of human placental membranes. Endocrinology. 1978 May;102(5):1485–1495. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-5-1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Thorsson A. V., Enberg G., Hall K. IGF-II binding on human lymphoid cells: demonstration of a common high affinity receptor for insulin like peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):774–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Cuatrecasas P. Monensin blocks the maturation of receptors for insulin and somatomedin C: identification of receptor precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1228–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Baxter R. C., Harrison L. C. Structural differences between insulin and somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors revealed by autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 30;109(2):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91744-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Harrison L. C. Disulphide reduction alters the immunoreactivity and increases the affinity of insulin-like growth-factor-I receptors in human placenta. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):417–423. doi: 10.1042/bj2360417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Harrison L. C. The human placenta contains two distinct binding and immunoreactive species of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2288–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Newman J. D., Harrison L. C. An atypical insulin receptor with high affinity for insulin-like growth factors copurified with placental insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Purification and primary structure of a polypeptide with multiplication-stimulating activity from rat liver cell cultures. Homology with human insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6859–6865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra P., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Structural and immunological characterization of insulin-like growth factor II binding to IM-9 cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Dec;63(6):1400–1405. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-6-1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody which can distinguish between two distinct species of the type I receptor for insulin-like growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1341–1347. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. D., Harrison L. C. Homogeneous bivalent insulin receptor: purification using insulin coupled to 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole activated-agarose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91914-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer C. L., Czech M. P. Purification of the type II insulin-like growth factor receptor from rat placenta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8539–8542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Methods for assessing immunologic and biologic properties of iodinated peptide hormones. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:223–233. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Cassell D. J., Wong K. Y., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor block insulin binding and inhibit insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7312–7316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Maddux B., Wong K. Y., Styne D. M., Van Vliet G., Humbel R. E., Goldfine I. D. Interactions of a monoclonal antibody to the insulin receptor with receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Endocrinology. 1983 May;112(5):1865–1867. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-5-1865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K., Baron M. D., Heward J. M., Luzio J. P., Bellatin J., Lennox E. S. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with multiple epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):199–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2350199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Klapper D. G., Fellows R. E., Grissom F. E., Schlueter R. J. Purification of somatomedin-C from human plasma: chemical and biological properties, partial sequence analysis, and relationship to other somatomedins. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):790–797. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Dons R. F., Hernandez E., Roth J., Gorden P. Insulin resistance associated with androgen excess in women with autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):851–855. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Thompson K., Petersen D. J. Separation of the high affinity insulin-like growth factor I receptor from low affinity binding sites by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16461–16469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


