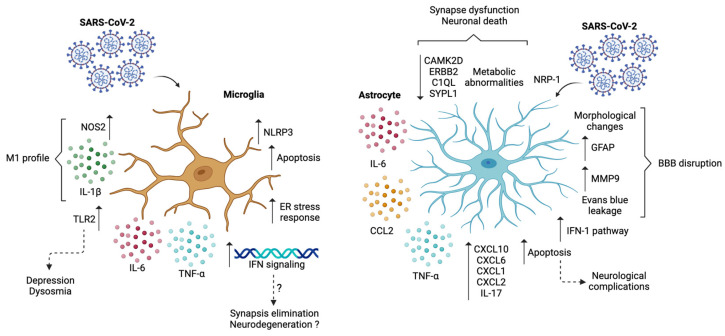
Figure 2.
Effect of SARS-CoV-2 on microglia and astrocytes. The cell responses of microglia after SARS-CoV-2 infection indicate a polarization towards an M1 pro-inflammatory profile and an increase in apoptosis, ER stress response, NLRP3 inflammasome components, IFN signaling, possibly leading to synapsis elimination and neurodegeneration. The infection also causes TLR2 activation, which is associated with depression and dysosmia. The cell responses of astrocytes after SARS-CoV-2 infection led to an activation of astrocytes, an increase in MMP9, morphological changes, and evidence of Evans blue dye leakage, suggesting a BBB disruption. There is also an increase in the IFN-I pathway, CXCL10, CXCL6, CXCL2, CXCL1, and IL-17, alongside the secretion of pro-inflammatory components TNF-α, IL-6, and CCL2. There is an increase in apoptosis and metabolic abnormalities, alongside a decrease in CAMK2D, ERBB2, C1QL, and SYPL1, which suggests neurological complications, synapse dysfunction, and neuronal death. (Created with Biorender; Agreement number #TC26KC0CKS).