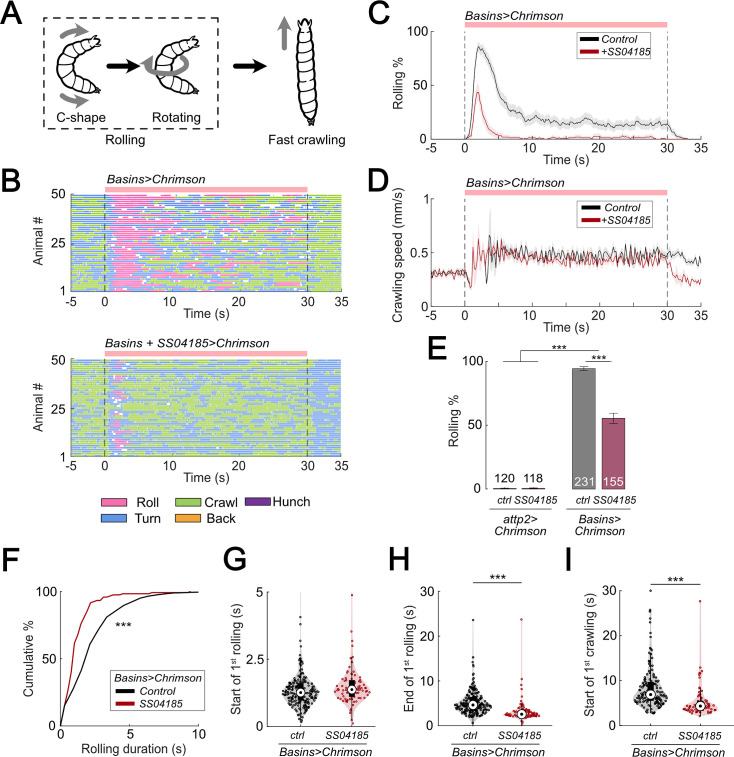
Figure 1. Activation of SS04185 inhibits rolling evoked by activation of Basin neurons.
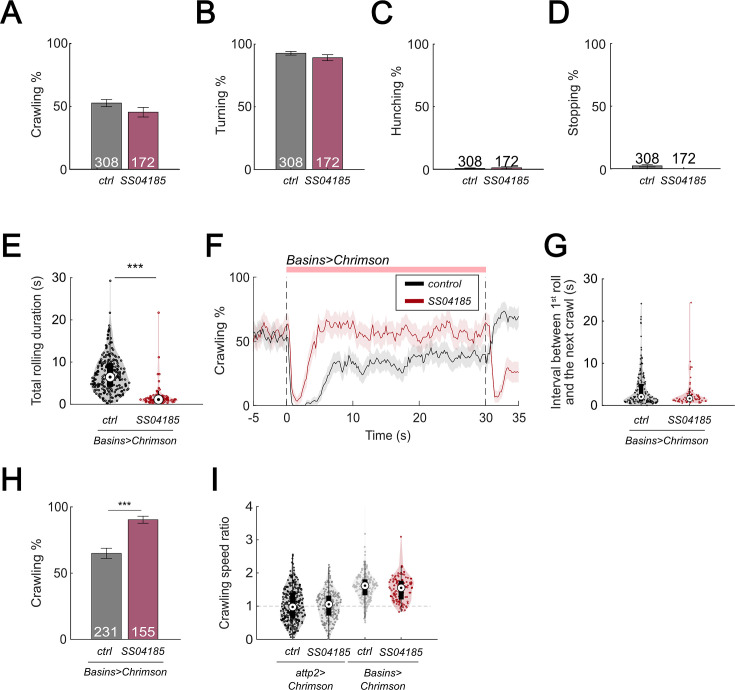
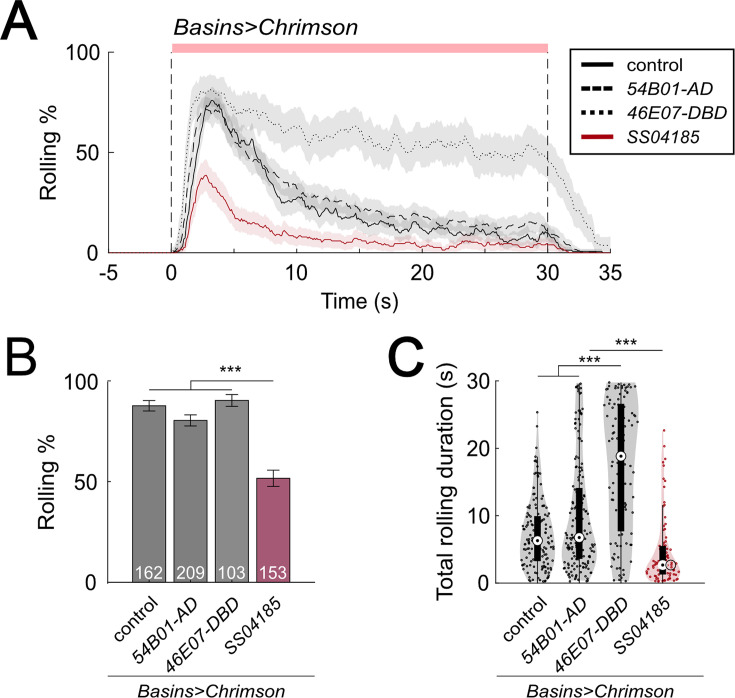
(A) Schematic of Drosophila larval escape behavior sequence. (B) Ethograms of Basin activation (top panel) and co-activation of SS04185 and Basins (bottom panel). Each row represents an individual larva. Pink, blue, green, orange, and purple lines represent bouts of rolling, turning, crawling, backward crawling, and hunching. The red bar and dashed lines indicate the time window during which neural activation was present. Genotypes: 20xUAS-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus/+;+; R72F11-Gal4/+ (top); 20xUAS-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus/+; R54B01-Gal4.AD/+; R46E07-Gal4.DBD/ R72F11-Gal4 (bottom). Genotypes in (C, D, F–I) are the same as those mentioned here. (C) Time series of larval crawling speed during co-activation of SS04185 and Basins (red) and activation of Basins alone (black). Shaded areas represent the standard error. The red bar and dashed lines denote the optogenetic stimulation window. (D) Time series of rolling probabilities of larvae during co-activation of SS04185 and Basins (red) and activation of Basins alone (black). Shaded areas represent 95% confidential intervals for rolling probabilities. The red bar and dashed lines denote the optogenetic stimulation window. (E) Rolling probabilities of larvae with activation of different neurons. Error bars represent the 95% confidence interval. Genotypes from left to right: (1) 20xUAS-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus/+;;, (2) 20xUAS-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus/+; R54B01-Gal4.AD/+; R46E07-Gal4.DBD/+, (3) 20xUAS-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus/+;; R72F11-Gal4/+, and (4) 20xUAS-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus/+; R54B01-Gal4.AD/+; R46E07-Gal4.DBD/ R72F11-Gal4. n = 120, 118, 231, 155 from left to right. Statistics: Chi-square test, χ2 = 0, p > 0.05 for the first two groups; χ2 = 83.85, p < 0.001 for the last two groups; and χ2 = 365.51, p < 0.001 for the comparison between the first two groups and the last two groups. (F) Cumulative plot of rolling duration. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001, n = 652, 120. (G) A violin plot showing start of first rolling bout for each larva during stimulation. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.027, n = 225, 89. (H) A violin plot displaying end of first rolling bout for each larva during stimulation. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001, n = 225, 89. (I) A violin plot presenting start of first crawling bout for each larva during stimulation. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001, n = 214, 70. ***p < 0.001.