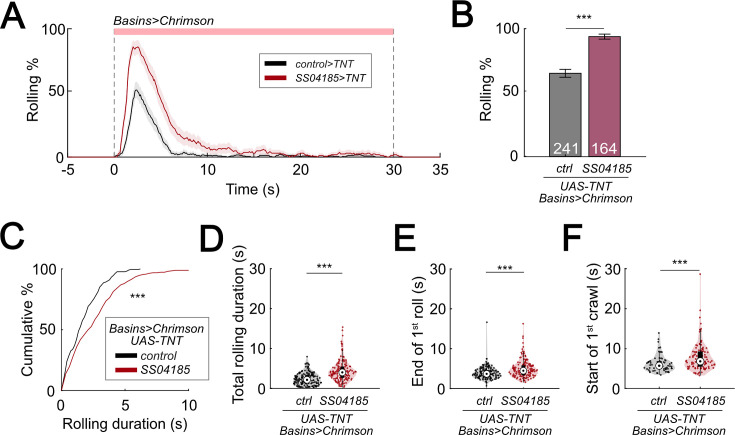
Figure 6. Inhibition of SeIN128 prolongs rolling and delays initiation of crawling.
(A) Time series of rolling probabilities of larvae with Basin activation (black), or SS04185 inhibition and Basin activation (red). Shaded regions show 95% confidential intervals of rolling probabilities. Genotypes: 13xLexAop2-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus; R72F11-LexA/+; UAS- TeTxLC.tnt/+ (black); 13xLexAop2-IVS-CsChrimson::mVenus; R72F11-LexA/R54B01-Gal4.AD; UAS-TeTxLC.tnt/R46E07-Gal4.DBD (red). Genotypes in (B–F) are the same as mentioned here. (B) Rolling probabilities during first 5 s of stimulation in (A). Error bars, 95% confidence interval. n = 241, 164. Statistics: Chi-square test, χ2 = 44.02, p < 0.001. (C) A violin plot of total time spent rolling for each individual larva during stimulation. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001, n = 221, 258. (D) Cumulative plot of rolling duration. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001, n = 160, 154. (E) A violin plot of end of first rolling bout for each larva during stimulation. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001, n = 160, 154. (F) A violin plot of start of first crawling bout for each larva during stimulation. Statistics: Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.001, n = 65, 105. ***p < 0.001.