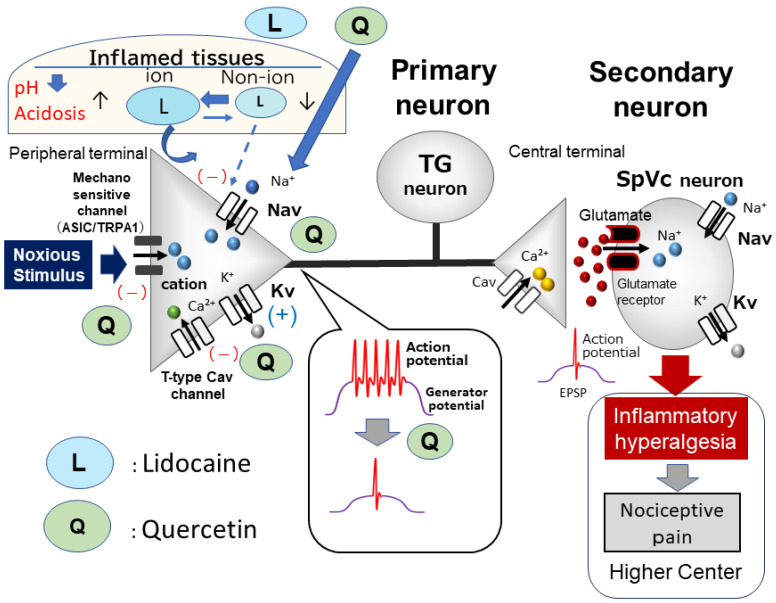
Figure 2.
Local anesthetic effect of quercetin under inflammatory conditions. The inhibitory effect of quercetin on inflamed tissues may be caused by the suppression of the firing frequency of action potentials by the inhibition of nociceptive mechanosensitive channels (ASIC and TRPA1), the inhibition of Nav channels, the inhibition of T-type Cav channels, and the opening of Kv channels. The inhibitory potency of quercetin on the discharge frequency is significantly higher than that of lidocaine; therefore, quercetin has a strong local anesthetic effect on inflamed tissues and is expected to be used in the field of complementary and alternative medicine. EPSP = excitatory postsynaptic potential.