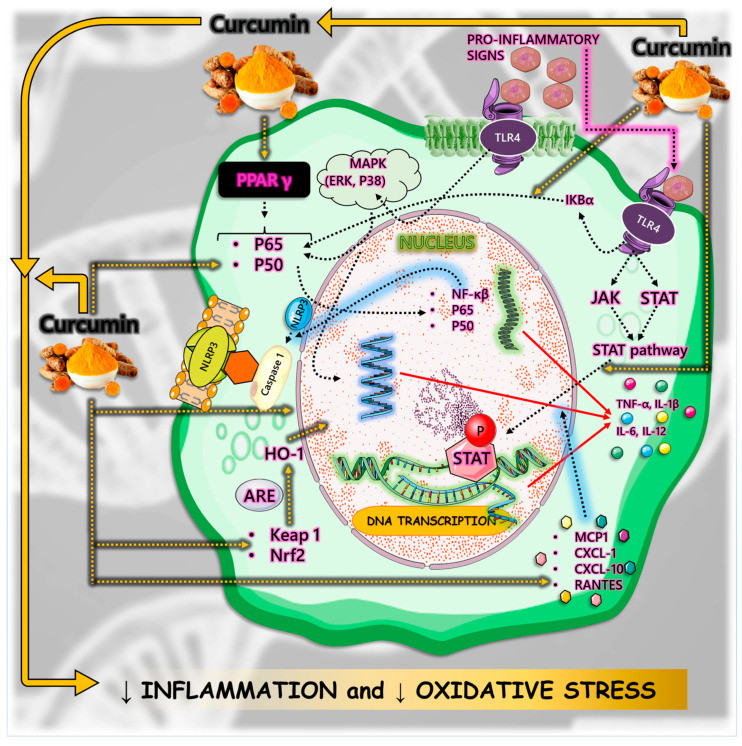
Figure 4.
The effects of curcumin against inflammatory pathways. Curcumin inhibits the MAPK, ERK, p38, p65, p50, and NFkB pathways and the consequent release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1; IL-12, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Besides that, curcumin also inhibits the Janus kinase/signal transducer and active factor of transcription (JAK-STAT) cascade. There is stimulation of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) and nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) that also interfere with pro-inflammatory pathways. ARE: antioxidant responsive elements;CXCL: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; ERK: protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; HO-1: Heme-oxygenase-1; IKB: IkappaB kinase; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCP1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; NF-κβ: nuclear factor-kappa beta,; NRLP34: NLR family pyrin domain containing; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; RANTES: IL-8 superfamily cytokines; TLR4: Toll-like receptor. ↓: decrease.